Simultaneous Optimized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit with Application to ECG Compression
Paper and Code
Jun 05, 2024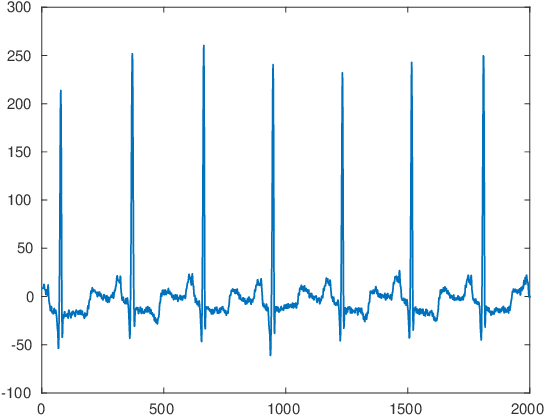
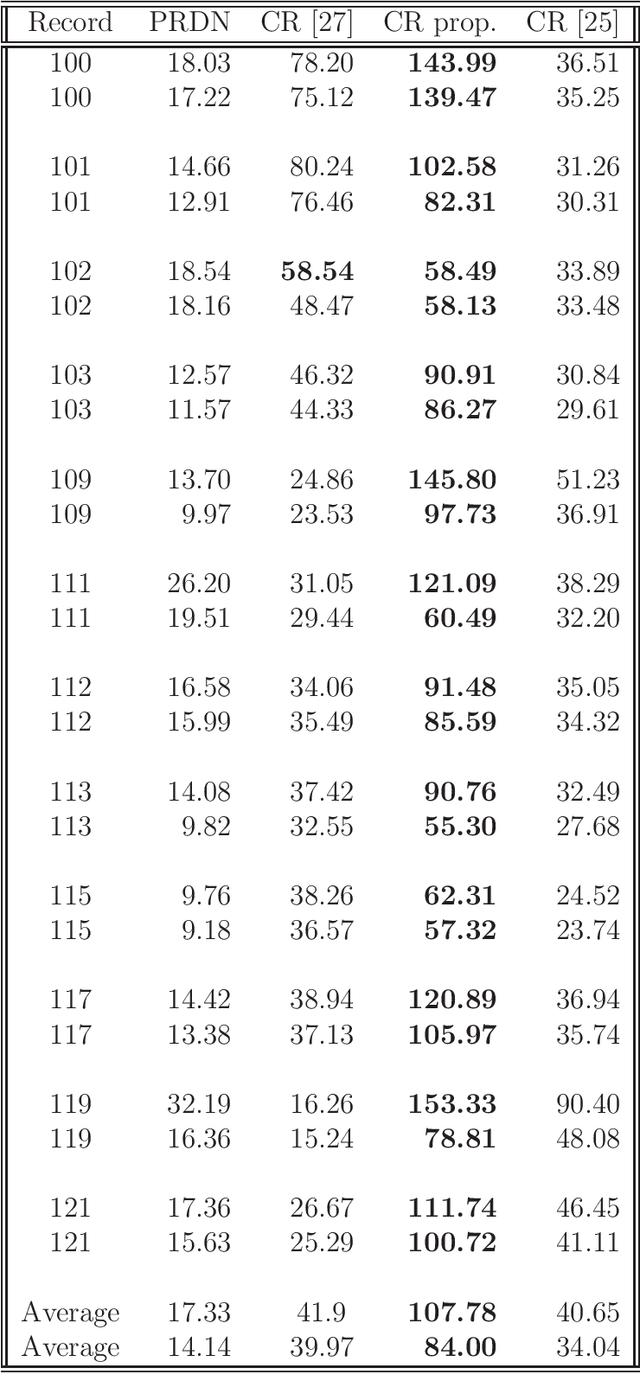
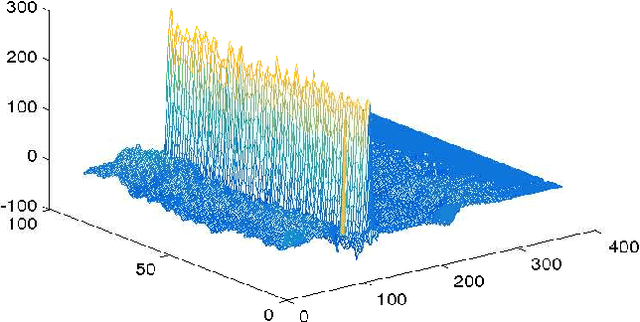
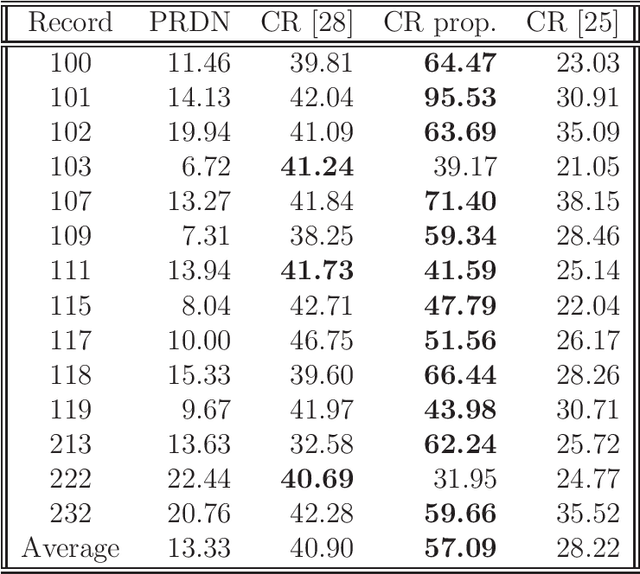
A greedy pursuit strategy which finds a common basis for approximating a set of similar signals is proposed. The strategy extends the Optimized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit approach to selecting the subspace containing the approximation of all the signals in the set. The method, called Simultaneous Optimized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit, is stepwise optimal in the sense of minimizing at each iteration the mean error norm of the joint approximation. When applied to compression of electrocardiograms, significant gains over other transformation based compression techniques are demonstrated on the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia dataset.
* Matlab software for implementing the approach has been made available
on http://www.nonlinear-approx.info/examples/node017.html
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge