Significant changes in EEG neural oscillations during different phases of three-dimensional multiple object tracking task (3D-MOT) imply different roles for attention and working memory
Paper and Code
Jul 29, 2022
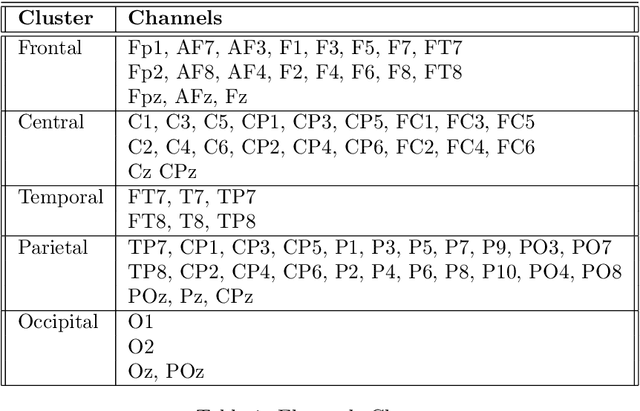
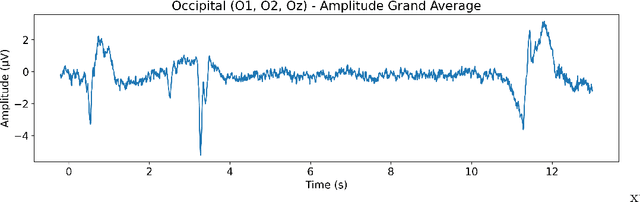
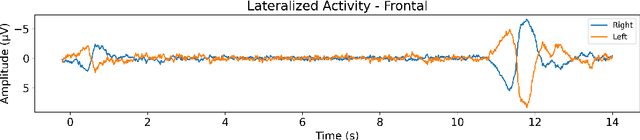
Our ability to track multiple objects in a dynamic environment enables us to perform everyday tasks such as driving, playing team sports, and walking in a crowded mall. Despite more than three decades of literature on multiple object tracking (MOT) tasks, the underlying and intertwined neural mechanisms remain poorly understood. Here we looked at the electroencephalography (EEG) neural correlates and their changes across the three phases of a 3D-MOT task, namely identification, tracking and recall. We recorded the EEG activity of 24 participants while they were performing a 3D-MOT task with either 1, 2 or 3 targets where some trials were lateralized and some were not. We observed what seems to be a handoff between focused attention and working memory processes when going from tracking to recall. Our findings revealed a strong inhibition in delta and theta frequencies from the frontal region during tracking, followed by a strong (re)activation of these same frequencies during recall. Our results also showed contralateral delay activity (CDA) for the lateralized trials, in both the identification and recall phases but not during tracking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge