Scheduling Techniques for Liver Segmentation: ReduceLRonPlateau Vs OneCycleLR
Paper and Code
Feb 13, 2022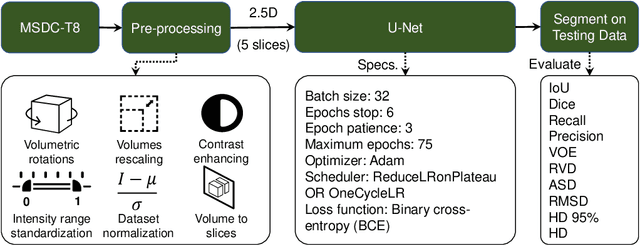
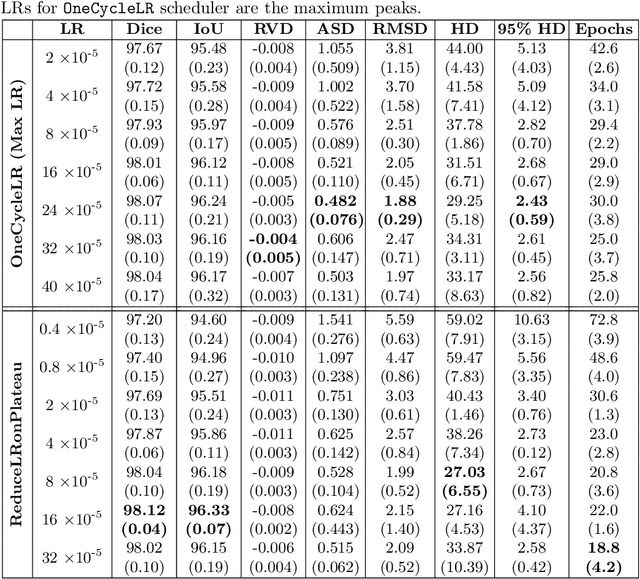
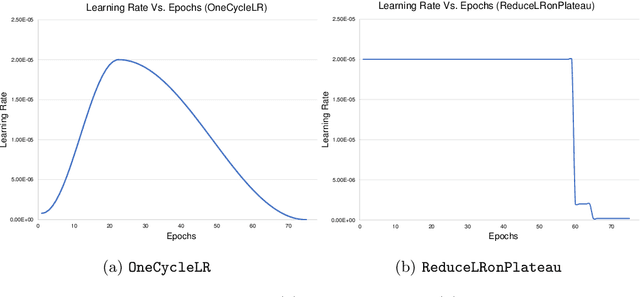
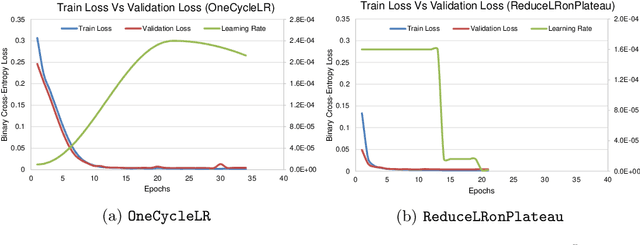
Machine learning and computer vision techniques have influenced many fields including the biomedical one. The aim of this paper is to investigate the important concept of schedulers in manipulating the learning rate (LR), for the liver segmentation task, throughout the training process, focusing on the newly devised OneCycleLR against the ReduceLRonPlateau. A dataset, published in 2018 and produced by the Medical Segmentation Decathlon Challenge organizers, called Task 8 Hepatic Vessel (MSDC-T8) has been used for testing and validation. The reported results that have the same number of maximum epochs (75), and are the average of 5-fold cross-validation, indicate that ReduceLRonPlateau converges faster while maintaining a similar or even better loss score on the validation set when compared to OneCycleLR. The epoch at which the peak LR occurs perhaps should be made early for the OneCycleLR such that the super-convergence feature can be observed. Moreover, the overall results outperform the state-of-the-art results from the researchers who published the liver masks for this dataset. To conclude, both schedulers are suitable for medical segmentation challenges, especially the MSDC-T8 dataset, and can be used confidently in rapidly converging the validation loss with a minimal number of epochs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge