Schedule Earth Observation satellites with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Nov 12, 2019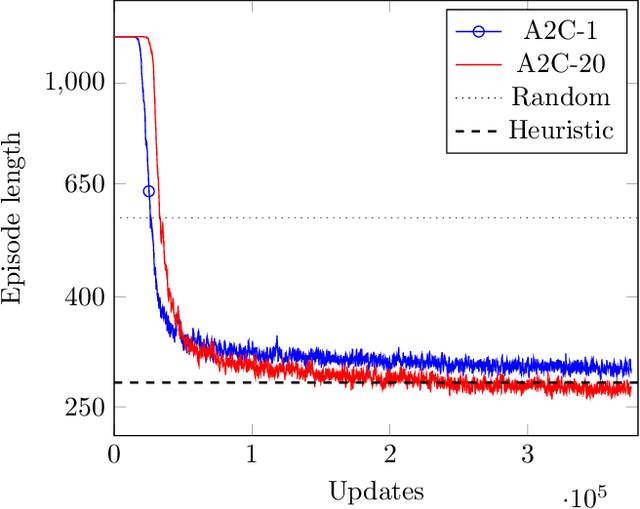
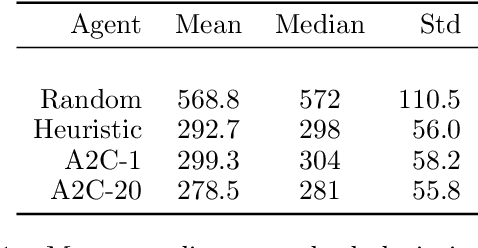
Optical Earth observation satellites acquire images worldwide , covering up to several million square kilometers every day. The complexity of scheduling acquisitions for such systems increases exponentially when considering the interoperabil-ity of several satellite constellations together with the uncertainties from weather forecasts. In order to deliver valid images to customers as fast as possible, it is crucial to acquire cloud-free images. Depending on weather forecasts, up to 50% of images acquired by operational satellites can be trashed due to excessive cloud covers, showing there is room for improvement. We propose an acquisition scheduling approach based on Deep Reinforcement Learning and experiment on a simplified environment. We find that it challenges classical methods relying on human-expert heuristic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge