Road Traffic Monitoring using DSRC Signals
Paper and Code
Dec 24, 2020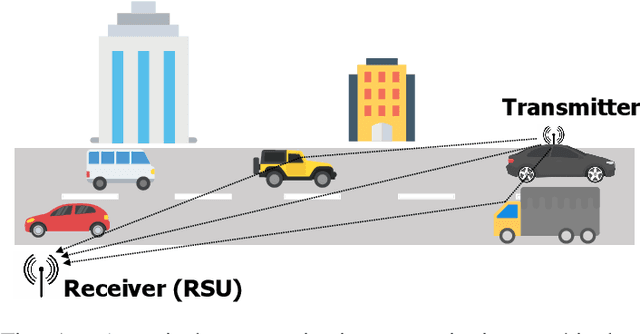



A wide variety of sensor technologies are nowadays used for traffic monitoring applications. Since most of these technologies rely on wired infrastructure, the installation and maintenance costs limit the deployment of the traffic monitoring systems. In this paper, we introduce a traffic monitoring approach that exploits dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) signals sent in a vehicular network and machine learning techniques. We verify the feasibility of the proposed approach with extensive simulations and real-world experiments at an intersection. We first simulate wireless channels under realistic traffic conditions using a ray-tracing simulator and a traffic simulator. Next, we conduct experiments in a real-world environment and collect DSRC messages transmitted from a roadside unit (RSU). The results show that we are able to separate different traffic intensities with an accuracy of 96.3\% and 87.6\% on the simulation and experimental data, respectively. We also estimate the number of vehicles on the road with a weighted mean absolute percentage error (WMAPE) of 10.7\% and 19.7\% on simulation and experimental data, respectively. The proposed approach is suitable to be deployed alongside the current monitoring systems to improve the performance of the systems without requiring additional investment in infrastructure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge