Reliable Deep Learning based Localization with CSI Fingerprints and Multiple Base Stations
Paper and Code
Nov 23, 2021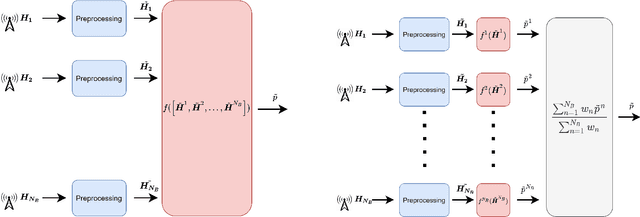
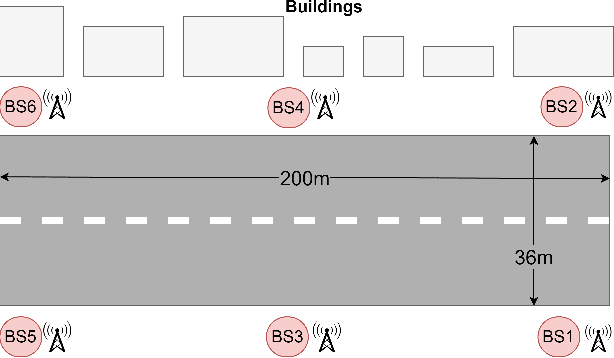
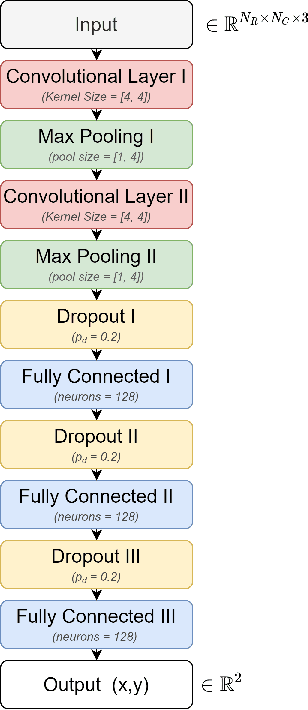
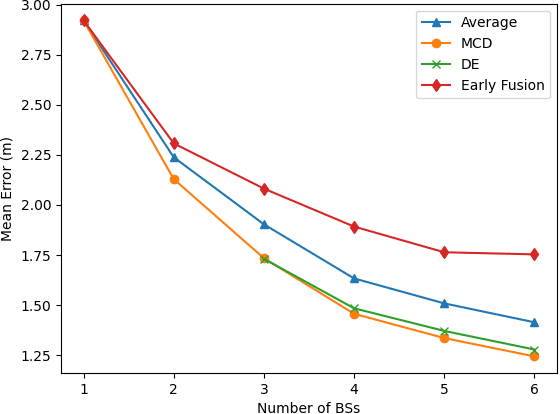
Deep learning (DL) methods have been recently proposed for user equipment (UE) localization in wireless communication networks, based on the channel state information (CSI) between a UE and each base station (BS) in the uplink. With the CSI from the available BSs, UE localization can be performed in different ways. One the one hand, a single neural network (NN) can be trained for the UE localization by considering the CSI from all the available BSs as one overall fingerprint of the user's location. On the other hand, the CSI at each BS can be used to obtain an estimate of the UE's position with a separate NN at each BS, and then the position estimates of all BSs are combined to obtain an overall estimate of the UE position. In this work, we show that UE localization with the latter approach can achieve a higher positioning accuracy. We propose to consider the uncertainty in the UE localization at each BS, such that overall UE's position is determined by combining the position estimates of the different BSs based on the uncertainty at each BS. With this approach, a more reliable position estimate can be obtained in case of variations in the channel.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge