Relational Embeddings for Language Independent Stance Detection
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2022
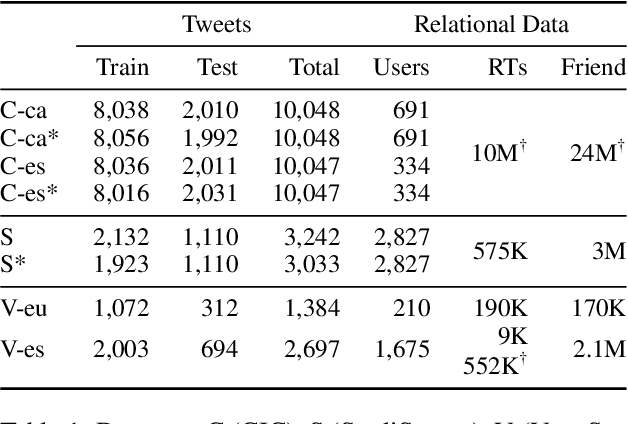

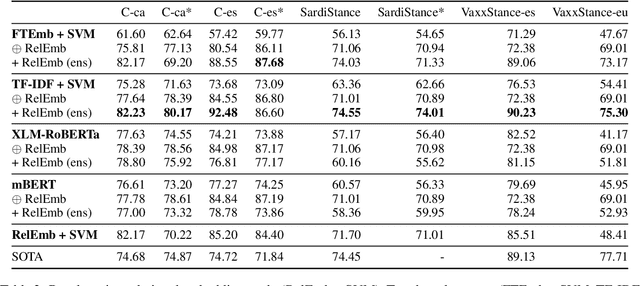
The large majority of the research performed on stance detection has been focused on developing more or less sophisticated text classification systems, even when many benchmarks are based on social network data such as Twitter. This paper aims to take on the stance detection task by placing the emphasis not so much on the text itself but on the interaction data available on social networks. More specifically, we propose a new method to leverage social information such as friends and retweets by generating relational embeddings, namely, dense vector representations of interaction pairs. Our method can be applied to any language and target without any manual tuning. Our experiments on seven publicly available datasets and four different languages show that combining our relational embeddings with textual methods helps to substantially improve performance, obtaining best results for six out of seven evaluation settings, outperforming strong baselines based on large pre-trained language models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge