Quasi-Chaotic Oscillators Based on Modular Quantum Circuits
Paper and Code
Mar 26, 2022

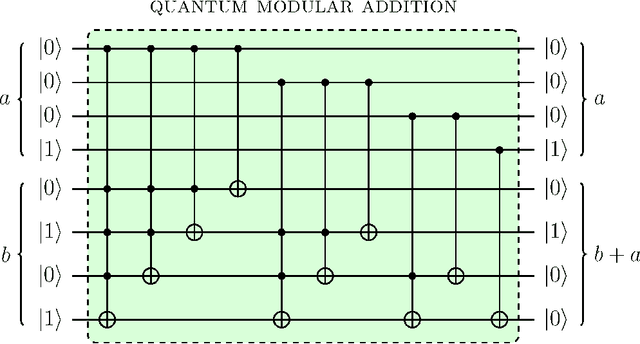
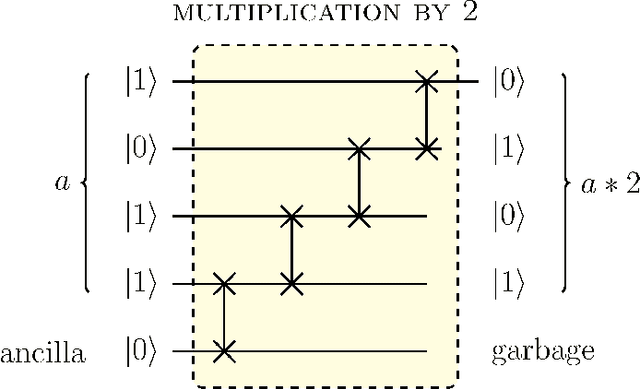
Digital circuits based on residue number systems have been considered to produce a pseudo-random behavior. The present work is an initial step towards the complete implementation of those systems for similar applications using quantum technology. We propose the implementation of a quasi-chaotic oscillator based on quantum modular addition and multiplication and we prove that quantum computing allows the parallel processing of data, paving the way for a fast and robust multi-channel encryption/decryption scheme. The resulting structure is assessed by several experiments in order to ascertain the desired noise-like behavior.
* 18 pages (one column), 9 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge