Playing optical tweezers with deep reinforcement learning: in virtual, physical and augmented environments
Paper and Code
Nov 10, 2020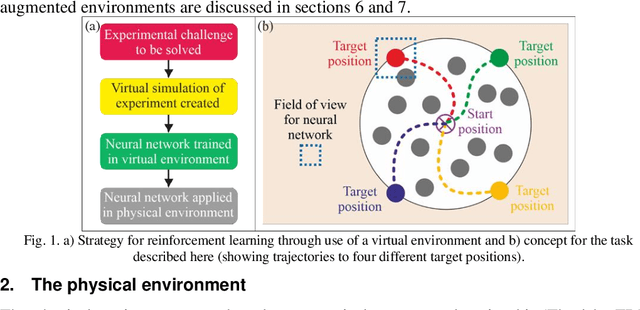
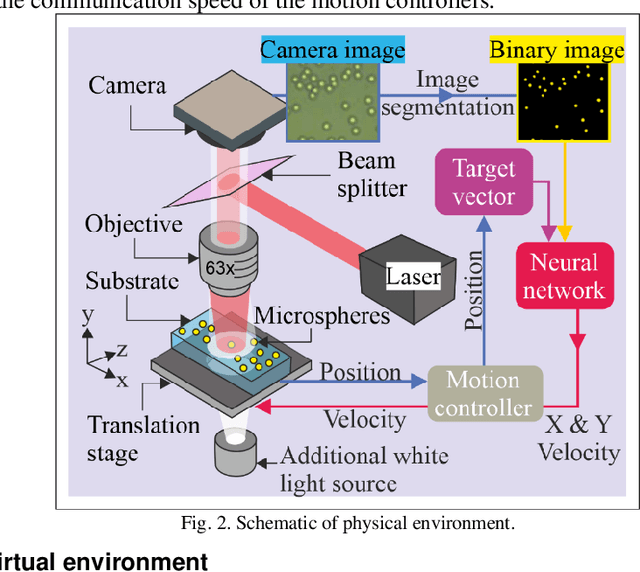
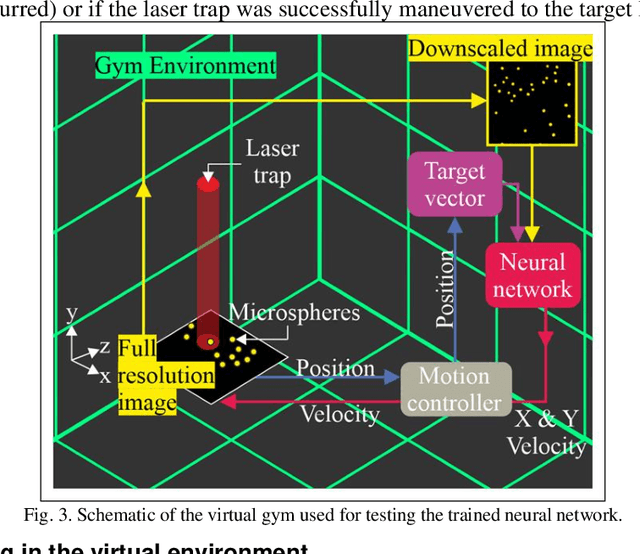
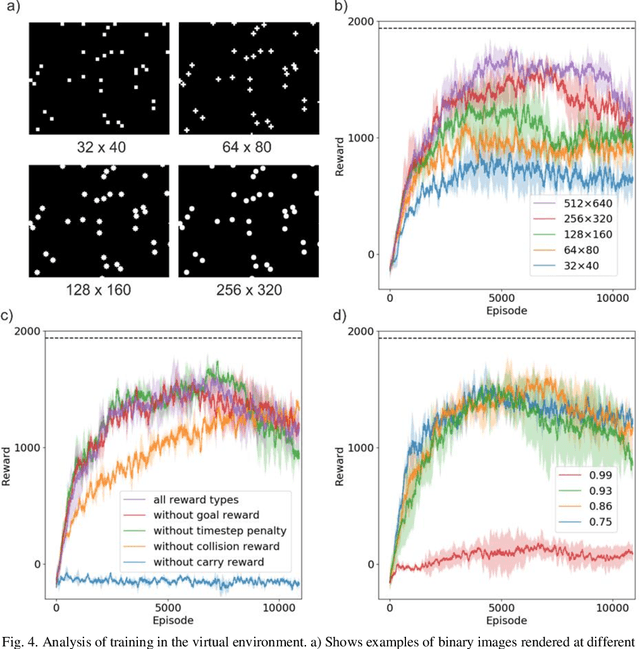
Reinforcement learning was carried out in a simulated environment to learn continuous velocity control over multiple motor axes. This was then applied to a real-world optical tweezers experiment with the objective of moving a laser-trapped microsphere to a target location whilst avoiding collisions with other free-moving microspheres. The concept of training a neural network in a virtual environment has significant potential in the application of machine learning for experimental optimization and control, as the neural network can discover optimal methods for problem solving without the risk of damage to equipment, and at a speed not limited by movement in the physical environment. As the neural network treats both virtual and physical environments equivalently, we show that the network can also be applied to an augmented environment, where a virtual environment is combined with the physical environment. This technique may have the potential to unlock capabilities associated with mixed and augmented reality, such as enforcing safety limits for machine motion or as a method of inputting observations from additional sensors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge