Personalization Effect on Emotion Recognition from Physiological Data: An Investigation of Performance on Different Setups and Classifiers
Paper and Code
Jul 20, 2016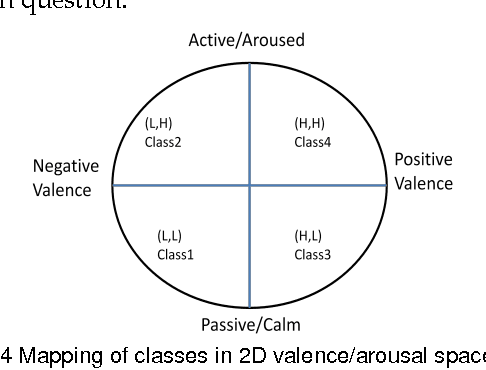
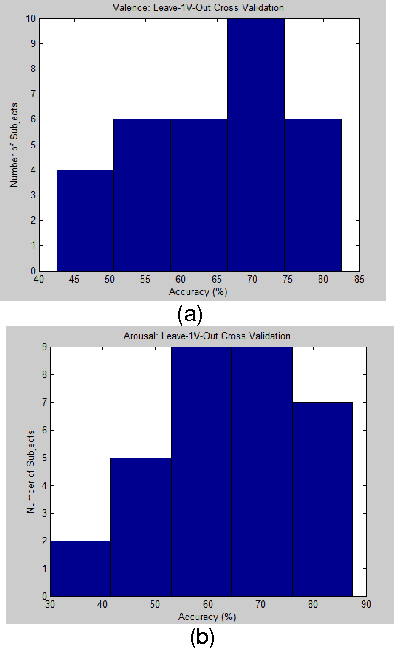
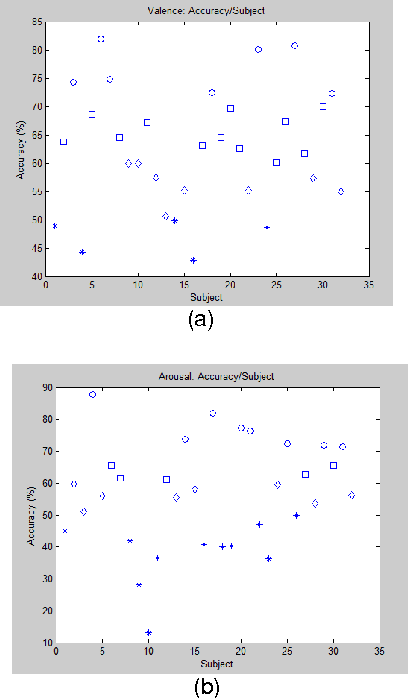
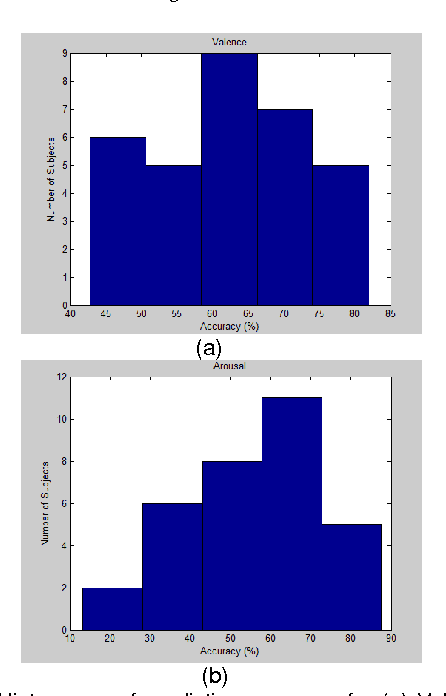
This paper addresses the problem of emotion recognition from physiological signals. Features are extracted and ranked based on their effect on classification accuracy. Different classifiers are compared. The inter-subject variability and the personalization effect are thoroughly investigated, through trial-based and subject-based cross-validation. Finally, a personalized model is introduced, that would allow for enhanced emotional state prediction, based on the physiological data of subjects that exhibit a certain degree of similarity, without the requirement of further feedback.
* 8 pages, 7 png figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge