PDL Impact on Linearly Coded Digital Phase Conjugation Techniques in CO-OFDM Systems
Paper and Code
Jun 27, 2021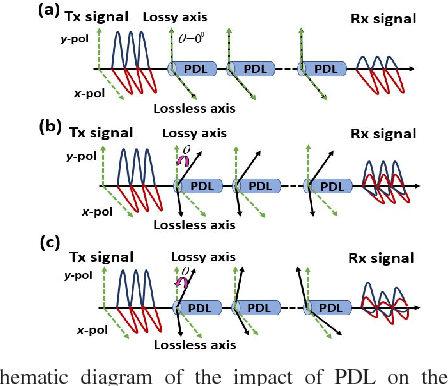
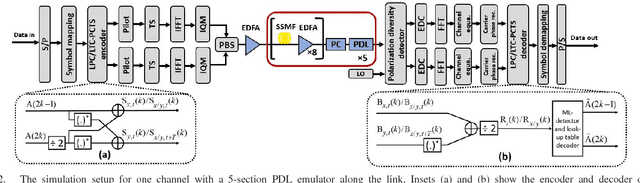
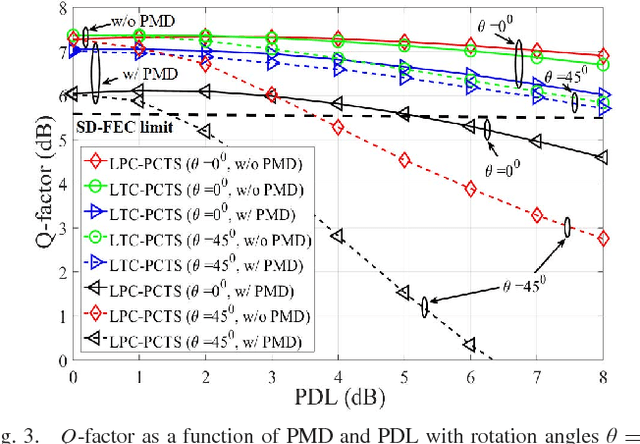
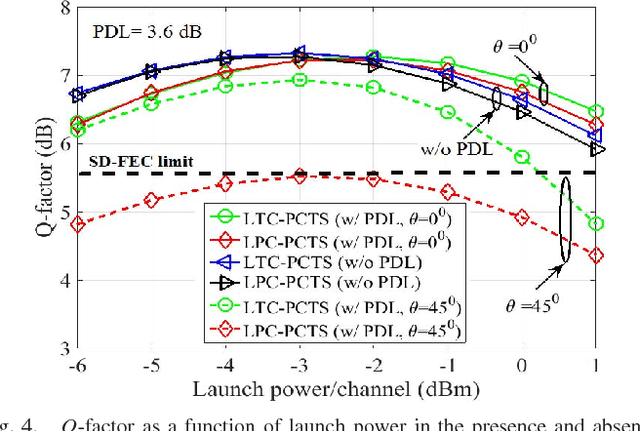
We investigate the impact of polarization-dependent loss (PDL) on the linearly coded digital phase conjugation (DPC) techniques in coherent optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (CO-OFDM) superchannel systems. We consider two DPC approaches: one uses orthogonal polarizations to transmit the linearly coded signal and its phase conjugate, while the other uses two orthogonal time slots of the same polarization. We compare the performances of these DPC approaches by considering both aligned- and statistical-PDL models. The investigation with aligned-PDL model indicates that the latter approach is more tolerant to PDL-induced distortions when compared to the former. Furthermore, the study using statistical-PDL model shows that the outage probability of the latter approach tends to zero at a root mean square PDL value of 3.6 dB. On the other hand, the former shows an outage probability of 0.63 for the same PDL value.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge