Optimizing example selection for retrieval-augmented machine translation with translation memories
Paper and Code
May 23, 2024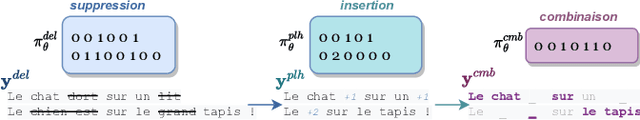
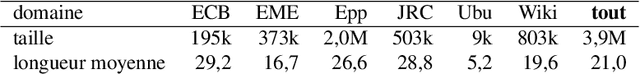
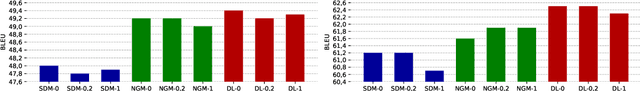
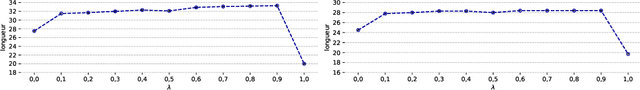
Retrieval-augmented machine translation leverages examples from a translation memory by retrieving similar instances. These examples are used to condition the predictions of a neural decoder. We aim to improve the upstream retrieval step and consider a fixed downstream edit-based model: the multi-Levenshtein Transformer. The task consists of finding a set of examples that maximizes the overall coverage of the source sentence. To this end, we rely on the theory of submodular functions and explore new algorithms to optimize this coverage. We evaluate the resulting performance gains for the machine translation task.
* TALN conference, French, 10 pages, 7 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge