Onboard Health Estimation using Distribution of Relaxation Times for Lithium-ion Batteries
Paper and Code
Oct 20, 2024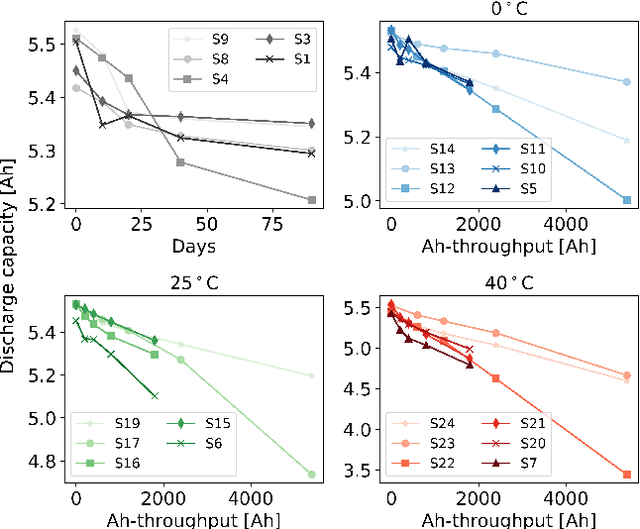
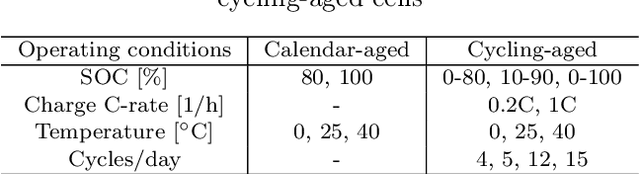
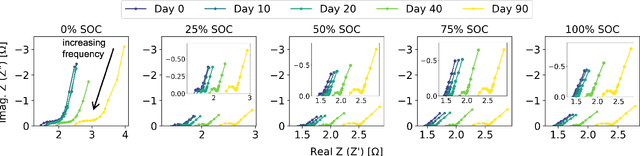
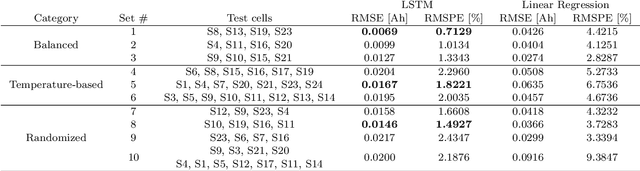
Real-life batteries tend to experience a range of operating conditions, and undergo degradation due to a combination of both calendar and cycling aging. Onboard health estimation models typically use cycling aging data only, and account for at most one operating condition e.g., temperature, which can limit the accuracy of the models for state-of-health (SOH) estimation. In this paper, we utilize electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) data from 5 calendar-aged and 17 cycling-aged cells to perform SOH estimation under various operating conditions. The EIS curves are deconvoluted using the distribution of relaxation times (DRT) technique to map them onto a function $\textbf{g}$ which consists of distinct timescales representing different resistances inside the cell. These DRT curves, $\textbf{g}$, are then used as inputs to a long short-term memory (LSTM)-based neural network model for SOH estimation. We validate the model performance by testing it on ten different test sets, and achieve an average RMSPE of 1.69% across these sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge