On Image Filtering, Noise and Morphological Size Intensity Diagrams
Paper and Code
Dec 17, 2004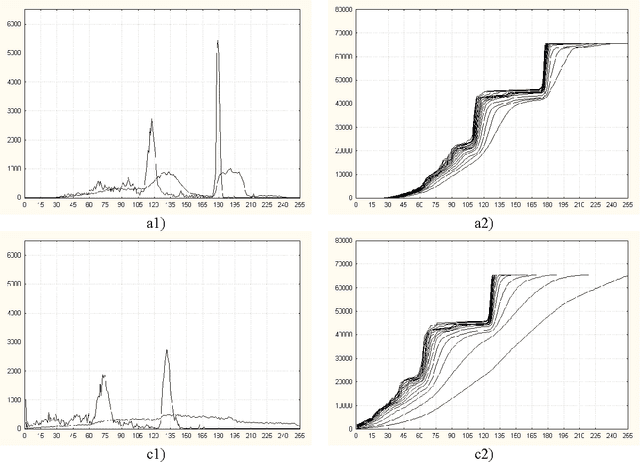

In the absence of a pure noise-free image it is hard to define what noise is, in any original noisy image, and as a consequence also where it is, and in what amount. In fact, the definition of noise depends largely on our own aim in the whole image analysis process, and (perhaps more important) in our self-perception of noise. For instance, when we perceive noise as disconnected and small it is normal to use MM-ASF filters to treat it. There is two evidences of this. First, in many instances there is no ideal and pure noise-free image to compare our filtering process (nothing but our self-perception of its pure image); second, and related with this first point, MM transformations that we chose are only based on our self - and perhaps - fuzzy notion. The present proposal combines the results of two MM filtering transformations (FT1, FT2) and makes use of some measures and quantitative relations on their Size/Intensity Diagrams to find the most appropriate noise removal process. Results can also be used for finding the most appropriate stop criteria, and the right sequence of MM operators combination on Alternating Sequential Filters (ASF), if these measures are applied, for instance, on a Genetic Algorithm's target function.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge