Next Challenges in Bringing Artificial Immune Systems to Production in Network Security
Paper and Code
May 13, 2008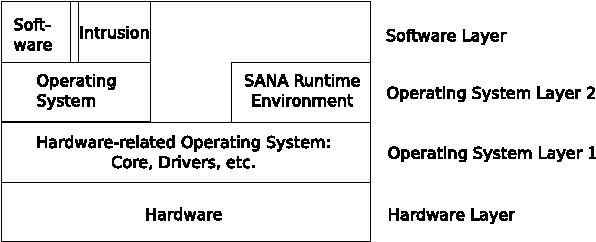
The human immune system protects the human body against various pathogens like e.g. biological viruses and bacteria. Artificial immune systems reuse the architecture, organization, and workflows of the human immune system for various problems in computer science. In the network security, the artificial immune system is used to secure a network and its nodes against intrusions like viruses, worms, and trojans. However, these approaches are far away from production where they are academic proof-of-concept implementations or use only a small part to protect against a certain intrusion. This article discusses the required steps to bring artificial immune systems into production in the network security domain. It furthermore figures out the challenges and provides the description and results of the prototype of an artificial immune system, which is SANA called.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge