Motion Magnification Algorithms for Video-Based Breathing Monitoring
Paper and Code
Nov 29, 2022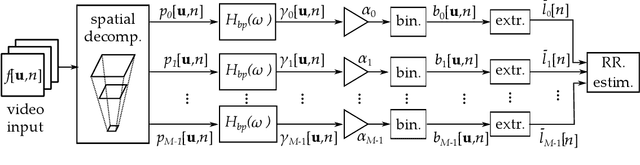
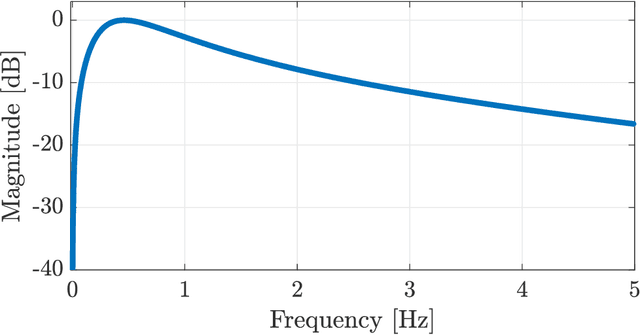
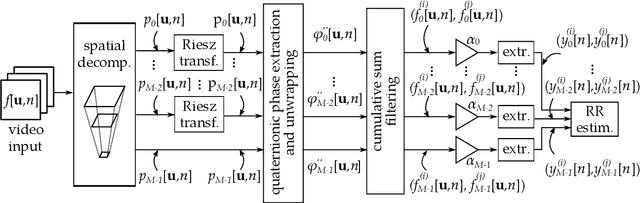
In this paper, we present two video processing techniques for contact-less estimation of the Respiratory Rate (RR) of framed subjects. Due to the modest extent of movements related to respiration in both infants and adults, specific algorithms to efficiently detect breathing are needed. For this reason, motion-related variations in video signals are exploited to identify respiration of the monitored patient and simultaneously estimate the RR over time. Our estimation methods rely on two motion magnification algorithms that are exploited to enhance the subtle respiration-related movements. In particular, amplitude- and phase-based algorithms for motion magnification are considered to extract reliable motion signals. The proposed estimation systems perform both spatial decomposition of the video frames combined with proper temporal filtering to extract breathing information. After periodic (or quasi-periodic) respiratory signals are extracted and jointly analysed, we apply the Maximum Likelihood (ML) criterion to estimate the fundamental frequency, corresponding to the RR. The performance of the presented methods is first assessed by comparison with reference data. Videos framing different subjects, i.e., newborns and adults, are tested. Finally, the RR estimation accuracy of both methods is measured in terms of normalized Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge