Massive MIMO Beam Management in Sub-6 GHz 5G NR
Paper and Code
Apr 12, 2022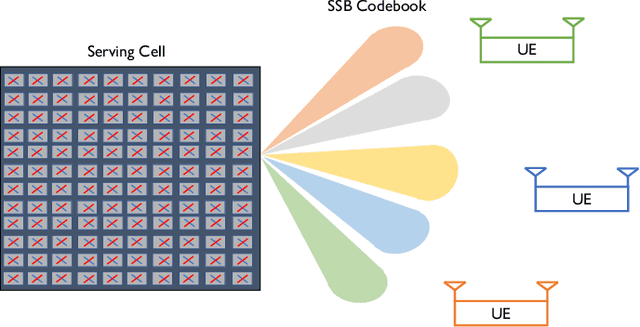
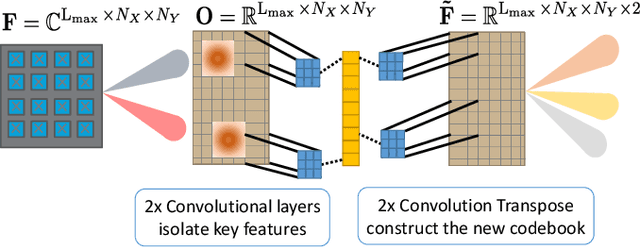
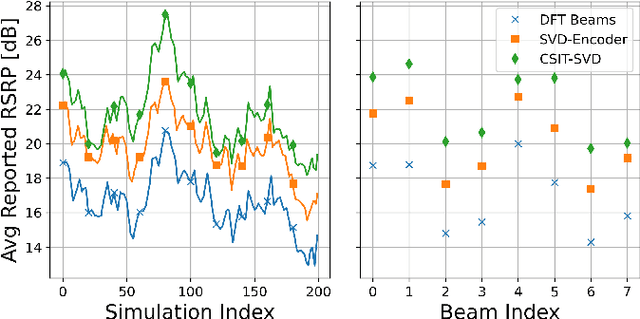
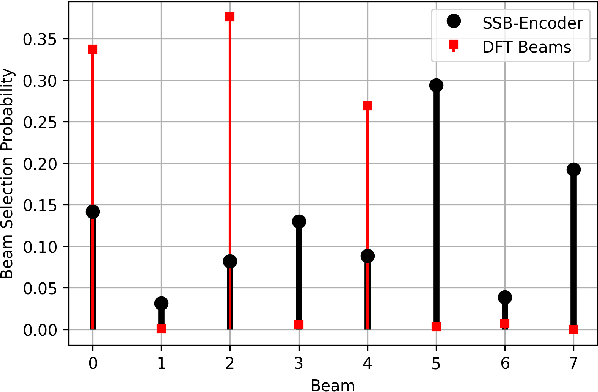
Beam codebooks are a new feature of massive multiple-input multiple-output (M-MIMO) in 5G new radio (NR). Codebooks comprised of beamforming vectors are used to transmit reference signals and obtain limited channel state information (CSI) from receivers via the codeword index. This enables large arrays that cannot otherwise obtain sufficient CSI. The performance, however, is limited by the codebook design. In this paper, we show that machine learning can be used to train site-specific codebooks for initial access. We design a neural network based on an autoencoder architecture that uses a beamspace observation in combination with RF environment characteristics to improve the synchronization signal (SS) burst codebook. We test our algorithm using a flexible dataset of channels generated from QuaDRiGa. The results show that our model outperforms the industry standard (DFT beams) and approaches the optimal performance (perfect CSI and singular value decomposition (SVD)-based beamforming), using only a few bits of feedback.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge