Map Segmentation by Colour Cube Genetic K-Mean Clustering
Paper and Code
Dec 17, 2004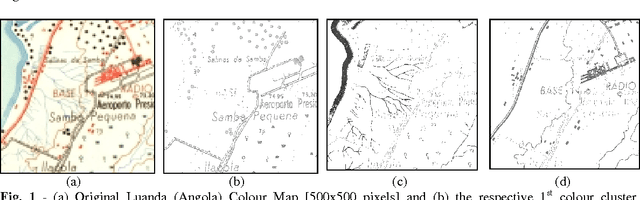
Segmentation of a colour image composed of different kinds of texture regions can be a hard problem, namely to compute for an exact texture fields and a decision of the optimum number of segmentation areas in an image when it contains similar and/or unstationary texture fields. In this work, a method is described for evolving adaptive procedures for these problems. In many real world applications data clustering constitutes a fundamental issue whenever behavioural or feature domains can be mapped into topological domains. We formulate the segmentation problem upon such images as an optimisation problem and adopt evolutionary strategy of Genetic Algorithms for the clustering of small regions in colour feature space. The present approach uses k-Means unsupervised clustering methods into Genetic Algorithms, namely for guiding this last Evolutionary Algorithm in his search for finding the optimal or sub-optimal data partition, task that as we know, requires a non-trivial search because of its NP-complete nature. To solve this task, the appropriate genetic coding is also discussed, since this is a key aspect in the implementation. Our purpose is to demonstrate the efficiency of Genetic Algorithms to automatic and unsupervised texture segmentation. Some examples in Colour Maps are presented and overall results discussed. KEYWORDS: Genetic Algorithms, Artificial Neoteny, Dynamic Mutation Rates, Faster Convergence, Colour Image Segmentation, Classification, Clustering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge