Machine learning as a flaring storm warning machine: Was a warning machine for the September 2017 solar flaring storm possible?
Paper and Code
Jul 05, 2020
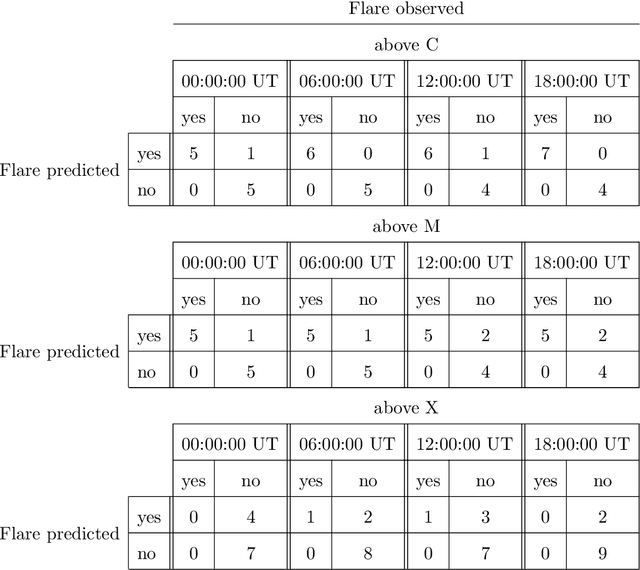
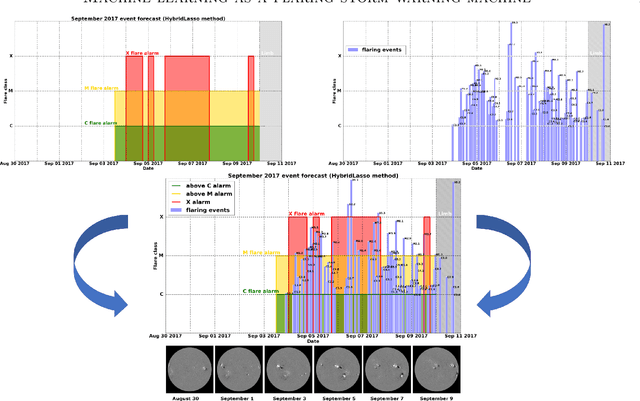
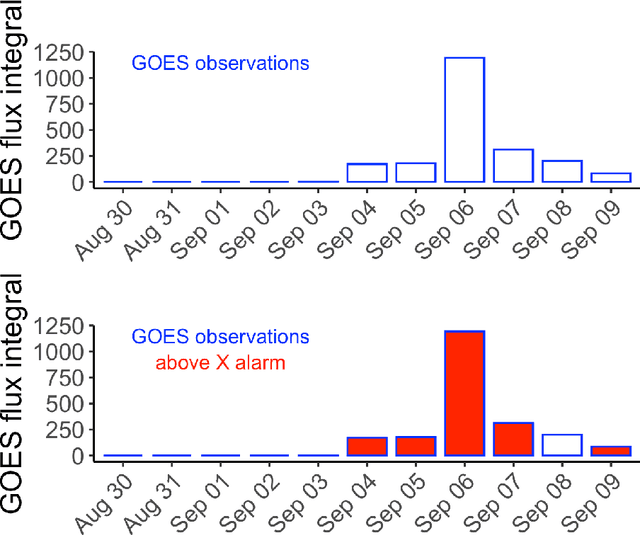
Machine learning is nowadays the methodology of choice for flare forecasting and supervised techniques, in both their traditional and deep versions, are becoming the most frequently used ones for prediction in this area of space weather. Yet, machine learning has not been able so far to realize an operating warning system for flaring storms and the scientific literature of the last decade suggests that its performances in the prediction of intense solar flares are not optimal. The main difficulties related to forecasting solar flaring storms are probably two. First, most methods are conceived to provide probabilistic predictions and not to send binary yes/no indications on the consecutive occurrence of flares along an extended time range. Second, flaring storms are typically characterized by the explosion of high energy events, which are seldom recorded in the databases of space missions; as a consequence, supervised methods are trained on very imbalanced historical sets, which makes them particularly ineffective for the forecasting of intense flares. Yet, in this study we show that supervised machine learning could be utilized in a way to send timely warnings about the most violent and most unexpected flaring event of the last decade, and even to predict with some accuracy the energy budget daily released by magnetic reconnection during the whole time course of the storm. Further, we show that the combination of sparsity-enhancing machine learning and feature ranking could allow the identification of the prominent role that energy played as an Active Region property in the forecasting process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge