Joint Source-Environment Adaptation for Deep Learning-Based Underwater Acoustic Source Ranging
Paper and Code
Mar 30, 2025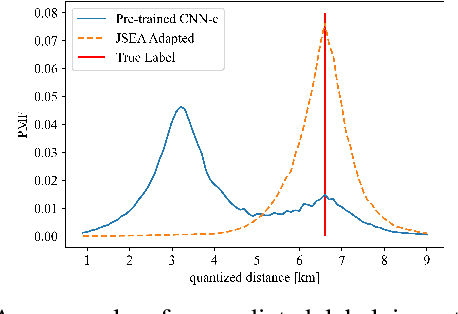
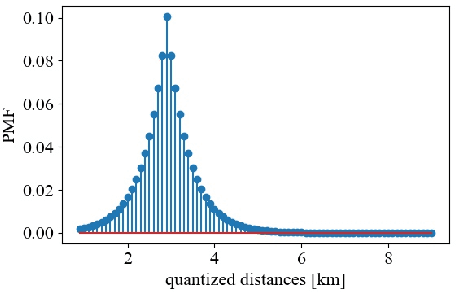
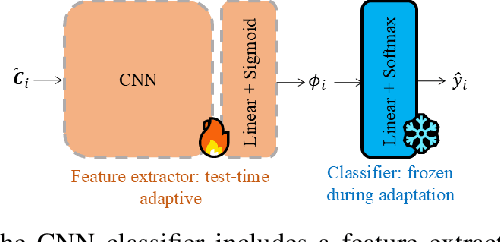
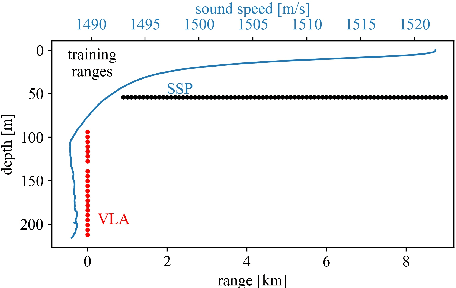
In this paper, we propose a method to adapt a pre-trained deep-learning-based model for underwater acoustic localization to a new environment. We use unsupervised domain adaptation to improve the generalization performance of the model, i.e., using an unsupervised loss, fine-tune the pre-trained network parameters without access to any labels of the target environment or any data used to pre-train the model. This method improves the pre-trained model prediction by coupling that with an almost independent estimation based on the received signal energy (that depends on the source). We show the effectiveness of this approach on Bellhop generated data in an environment similar to that of the SWellEx-96 experiment contaminated with real ocean noise from the KAM11 experiment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge