Joint Secure Design of Downlink and D2D Cooperation Strategies for Multi-User Systems
Paper and Code
Apr 13, 2021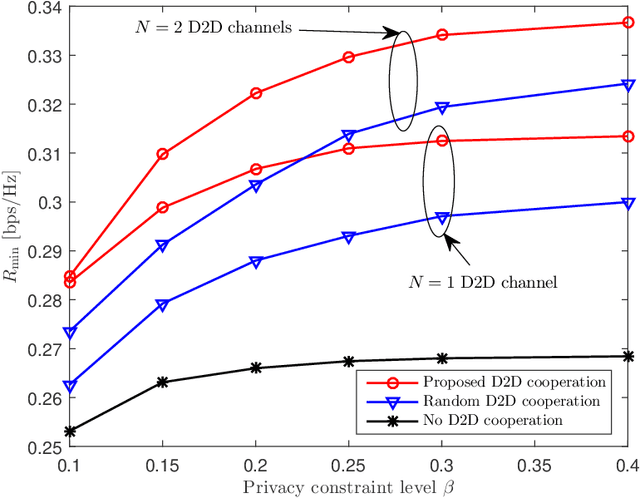
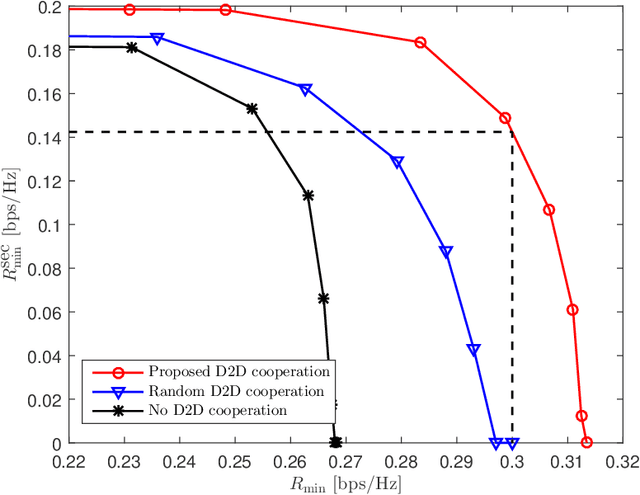
This work studies the role of inter-user device-to-device (D2D) cooperation for improving physical-layer secret communication in multi-user downlink systems. It is assumed that there are out-of-band D2D channels, on each of which a selected legitimate user transmits an amplified version of the received downlink signal to other legitimate users. A key technical challenge for designing such systems is that eavesdroppers can overhear downlink as well as D2D cooperation signals. We tackle the problem of jointly optimizing the downlink precoding, artificial noise covariance, and amplification coefficients that maximize the minimum rate. An iterative alternating optimization algorithm is proposed based on the matrix fractional programming. Numerical results confirm the performance gains of the proposed D2D cooperation scheme compared to benchmark secret communication schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge