Iris Recognition with Image Segmentation Employing Retrained Off-the-Shelf Deep Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jan 04, 2019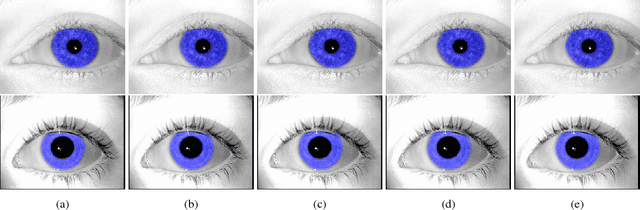
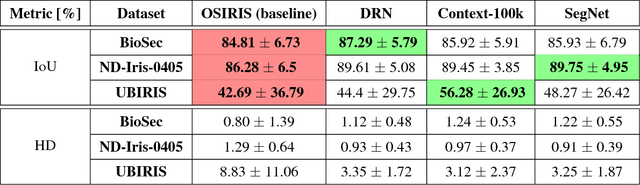

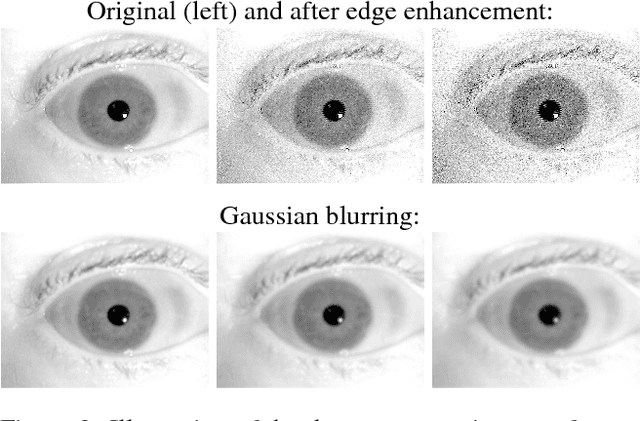
This paper offers three new, open-source, deep learning-based iris segmentation methods, and the methodology how to use irregular segmentation masks in a conventional Gabor-wavelet-based iris recognition. To train and validate the methods, we used a wide spectrum of iris images acquired by different teams and different sensors and offered publicly, including data taken from CASIA-Iris-Interval-v4, BioSec, ND-Iris-0405, UBIRIS, Warsaw-BioBase-Post-Mortem-Iris v2.0 (post-mortem iris images), and ND-TWINS-2009-2010 (iris images acquired from identical twins). This varied training data should increase the generalization capabilities of the proposed segmentation techniques. In database-disjoint training and testing, we show that deep learning-based segmentation outperforms the conventional (OSIRIS) segmentation in terms of Intersection over Union calculated between the obtained results and manually annotated ground-truth. Interestingly, the Gabor-based iris matching is not always better when deep learning-based segmentation is used, and is on par with the method employing Daugman's based segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge