Instagram Filter Removal on Fashionable Images
Paper and Code
Apr 11, 2021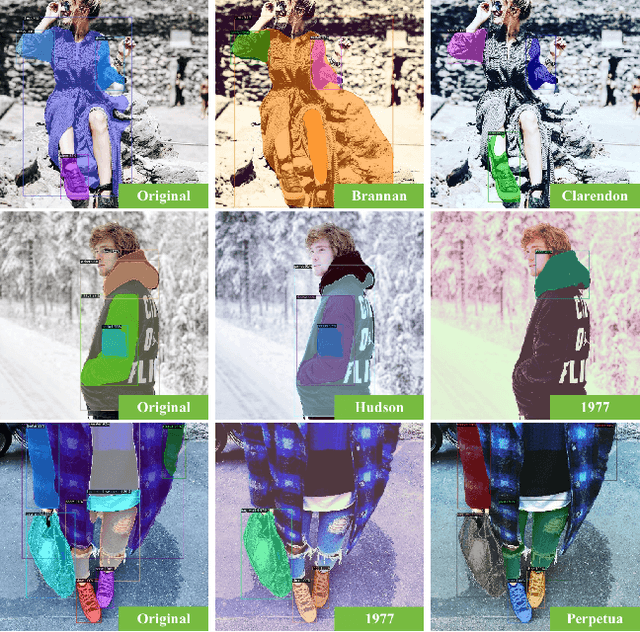
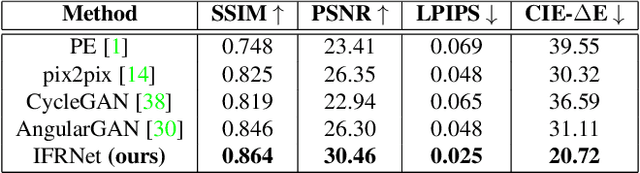

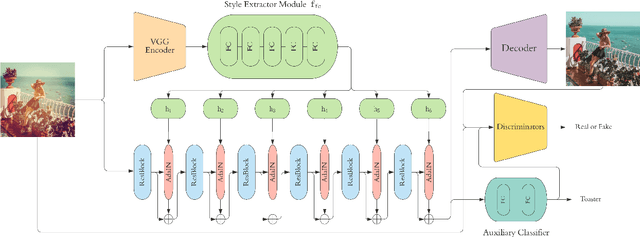
Social media images are generally transformed by filtering to obtain aesthetically more pleasing appearances. However, CNNs generally fail to interpret both the image and its filtered version as the same in the visual analysis of social media images. We introduce Instagram Filter Removal Network (IFRNet) to mitigate the effects of image filters for social media analysis applications. To achieve this, we assume any filter applied to an image substantially injects a piece of additional style information to it, and we consider this problem as a reverse style transfer problem. The visual effects of filtering can be directly removed by adaptively normalizing external style information in each level of the encoder. Experiments demonstrate that IFRNet outperforms all compared methods in quantitative and qualitative comparisons, and has the ability to remove the visual effects to a great extent. Additionally, we present the filter classification performance of our proposed model, and analyze the dominant color estimation on the images unfiltered by all compared methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge