Inferring subhalo effective density slopes from strong lensing observations with neural likelihood-ratio estimation
Paper and Code
Aug 29, 2022
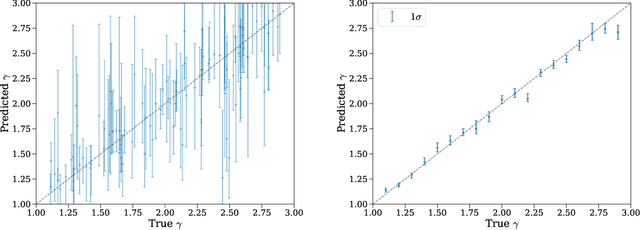
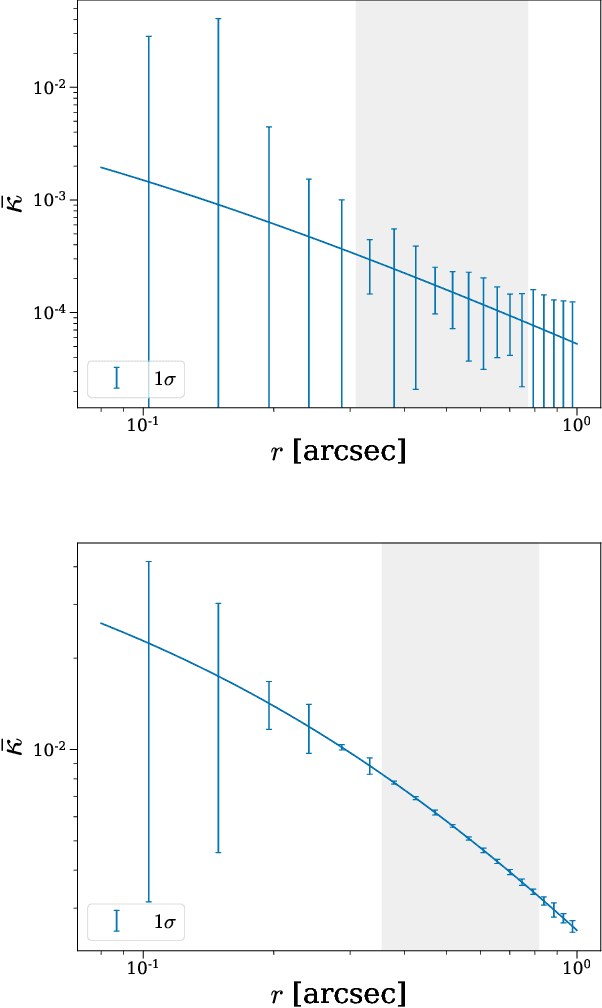
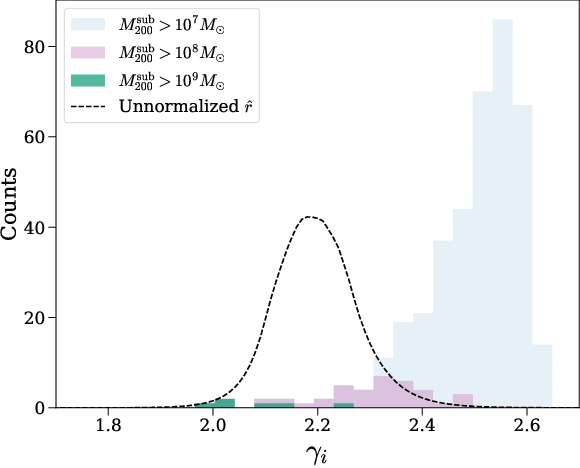
Strong gravitational lensing has emerged as a promising approach for probing dark matter models on sub-galactic scales. Recent work has proposed the subhalo effective density slope as a more reliable observable than the commonly used subhalo mass function. The subhalo effective density slope is a measurement independent of assumptions about the underlying density profile and can be inferred for individual subhalos through traditional sampling methods. To go beyond individual subhalo measurements, we leverage recent advances in machine learning and introduce a neural likelihood-ratio estimator to infer an effective density slope for populations of subhalos. We demonstrate that our method is capable of harnessing the statistical power of multiple subhalos (within and across multiple images) to distinguish between characteristics of different subhalo populations. The computational efficiency warranted by the neural likelihood-ratio estimator over traditional sampling enables statistical studies of dark matter perturbers and is particularly useful as we expect an influx of strong lensing systems from upcoming surveys.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge