IEDM, an Ontology for Irradiation Experiment Data Management
Paper and Code
Jan 16, 2019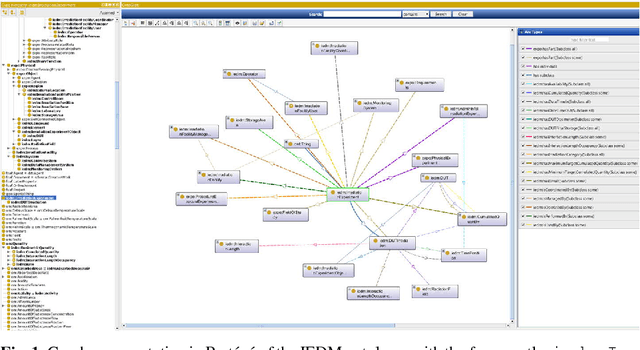
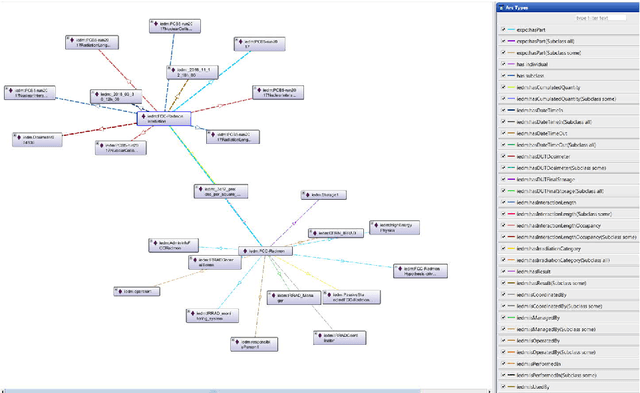
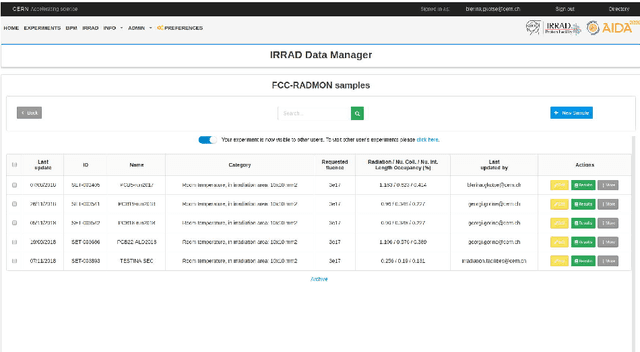
Irradiation experiments (IE) are an essential step in the development of High-Energy Physics (HEP) particle accelerators and detectors. They assess the radiation hardness of materials used in HEP experimental devices by simulating, in a short time, the common long-term degradation effects due to their bombardment by high-energy particles. IEs are also used in other scientific and industrial fields such as medicine (e.g., for cancer treatment, medical imaging, etc.), space/avionics (e.g., for radiation testing of payload equipment) as well as in industry (e.g., for food sterilization). Usually carried out with ionizing radiation, these complex processes require highly specialized infrastructures: the irradiation facilities. Currently, hundreds of such facilities exist worldwide. To help develop best practices and promote computer-assisted handling and management of IEs, we introduce IEDM, a new OWL-based Irradiation Experiment Data Management ontology. This paper provides an overview of the classes and properties of IEDM. Since one of the key design choices for IEDM was to maximize the reuse of existing foundational ontologies such as the Ontology of Scientific Experiments (EXPO), the Ontology of Units of Measure (OM) and the Friend-of-a-Friend Ontology (FOAF), we discuss the methodological issues of the integration of IEDM with these imported ontologies. We illustrate the use of IEDM via an actual IE recently performed at IRRAD, the CERN proton irradiation facility. Finally, we discuss other motivations for this work, including the use of IEDM for the generation of user interfaces for IE management, and their impact on our methodology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge