High-Resolution Peak Demand Estimation Using Generalized Additive Models and Deep Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Mar 07, 2022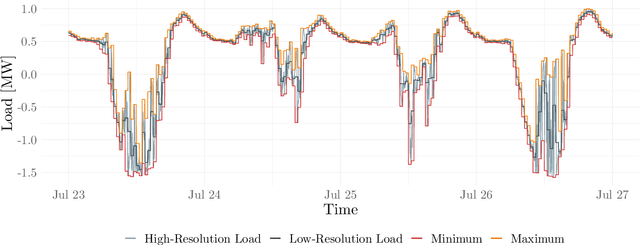
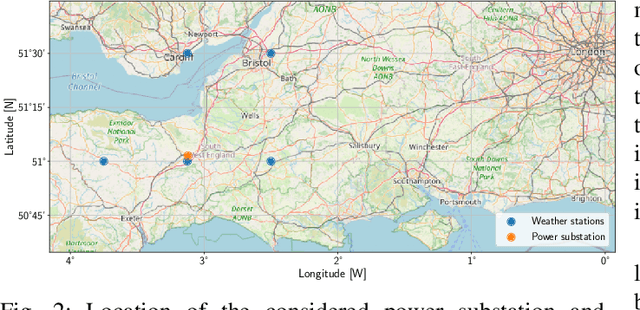
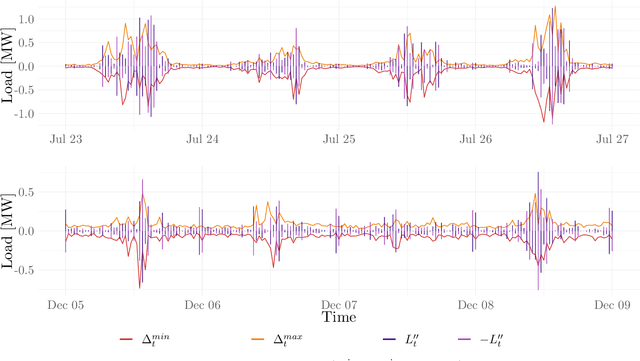
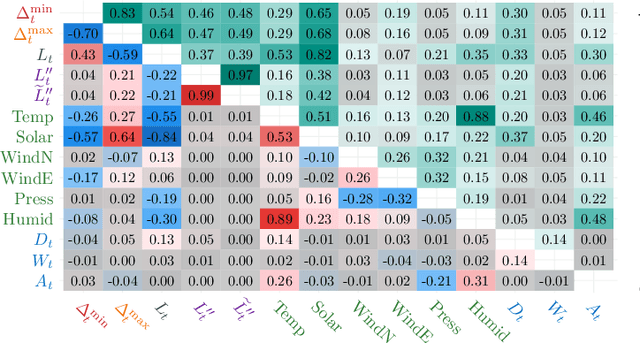
This paper presents a method for estimating high-resolution electricity peak demand given lower resolution data. The technique won a data competition organized by the British distribution network operator Western Power Distribution. The exercise was to estimate the minimum and maximum load values in a single substation in a one-minute resolution as precisely as possible. In contrast, the data was given in half-hourly and hourly resolutions. The winning method combines generalized additive models (GAM) and deep artificial neural networks (DNN) which are popular in load forecasting. We provide an extensive analysis of the prediction models, including the importance of input parameters with a focus on load, weather, and seasonal effects. In addition, we provide a rigorous evaluation study that goes beyond the competition frame to analyze the robustness. The results show that the proposed methods are superior, not only in the single competition month but also in the meaningful evaluation study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge