Hidden Effects of COVID-19 on Healthcare Workers: A Machine Learning Analysis
Paper and Code
Dec 12, 2021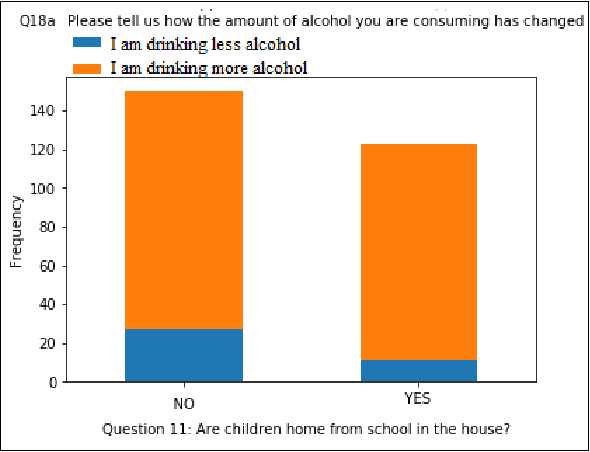

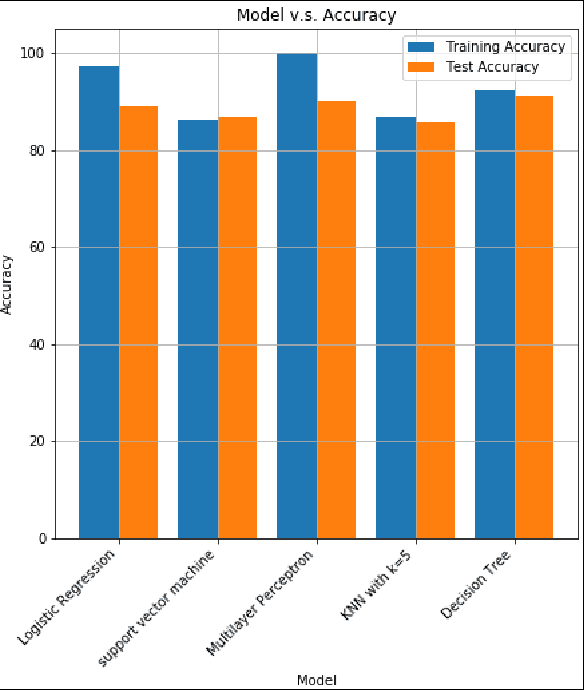
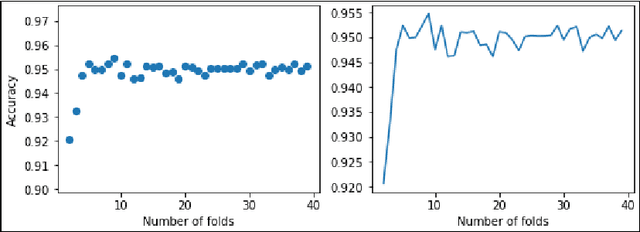
In this paper, we analyze some effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare workers. We specifically focus on alcohol consumption habit changes among healthcare workers using a mental health survey data obtained from the University of Michigan Inter-University Consortium for Political and Social Research. We use supervised and unsupervised machine learning methods and models such as Decision Trees, Logistic Regression, Naive Bayes classifier, k-Nearest Neighbors, Support Vector Machines, Multilayer perceptron, Random Forests, XGBoost, CatBoost, LightGBM, Synthetic Minority Oversampling, Chi-Squared Test and mutual information method to find out relationships between COVID-19 related negative effects and alcohol use changes in healthcare workers. Our findings suggest that some effects of the COVID-19 pandemic such as school closure, work schedule change and COVID-related news exposure may lead to an increase in alcohol use.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge