"hasSignification()": une nouvelle fonction de distance pour soutenir la détection de données personnelles
Paper and Code
Jun 14, 2022
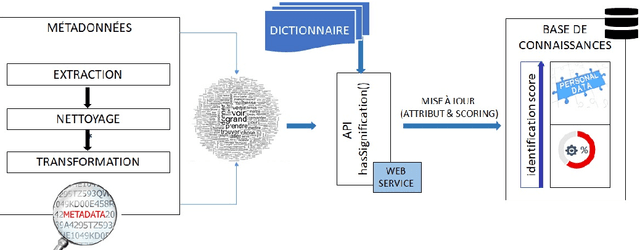
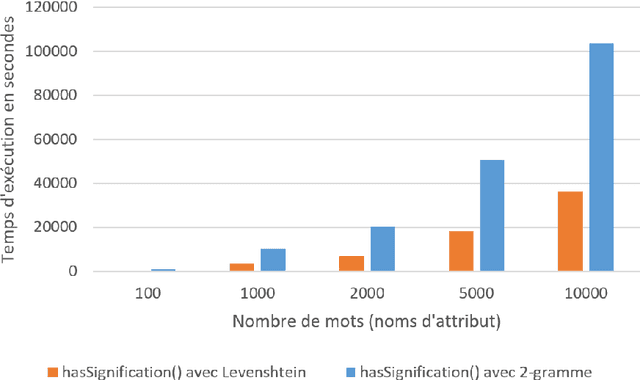
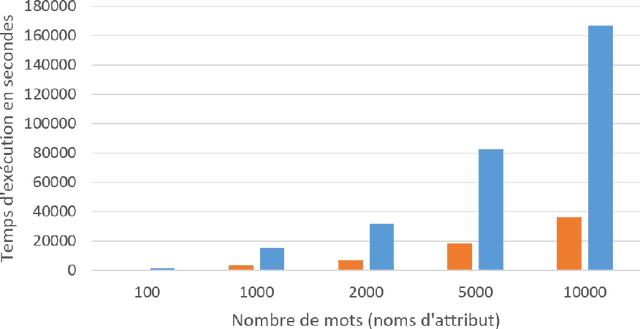
Today with Big Data and data lakes, we are faced of a mass of data that is very difficult to manage it manually. The protection of personal data in this context requires an automatic analysis for data discovery. Storing the names of attributes already analyzed in a knowledge base could optimize this automatic discovery. To have a better knowledge base, we should not store any attributes whose name does not make sense. In this article, to check if the name of an attribute has a meaning, we propose a solution that calculate the distances between this name and the words in a dictionary. Our studies on the distance functions like N-Gram, Jaro-Winkler and Levenshtein show limits to set an acceptance threshold for an attribute in the knowledge base. In order to overcome these limitations, our solution aims to strengthen the score calculation by using an exponential function based on the longest sequence. In addition, a double scan in dictionary is also proposed in order to process the attributes which have a compound name.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge