GAN-based Tabular Data Generator for Constructing Synopsis in Approximate Query Processing: Challenges and Solutions
Paper and Code
Dec 18, 2022


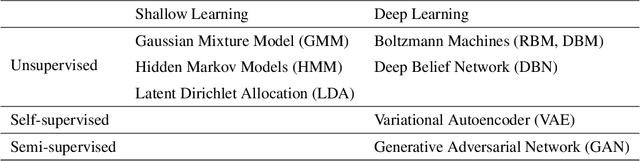
In data-driven systems, data exploration is imperative for making real-time decisions. However, big data is stored in massive databases that are difficult to retrieve. Approximate Query Processing (AQP) is a technique for providing approximate answers to aggregate queries based on a summary of the data (synopsis) that closely replicates the behavior of the actual data, which can be useful where an approximate answer to the queries would be acceptable in a fraction of the real execution time. In this paper, we discuss the use of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for generating tabular data that can be employed in AQP for synopsis construction. We first discuss the challenges associated with constructing synopses in relational databases and then introduce solutions to those challenges. Following that, we organized statistical metrics to evaluate the quality of the generated synopses. We conclude that tabular data complexity makes it difficult for algorithms to understand relational database semantics during training, and improved versions of tabular GANs are capable of constructing synopses to revolutionize data-driven decision-making systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge