FPGA Implementation of Simplified Spiking Neural Network
Paper and Code
Oct 02, 2020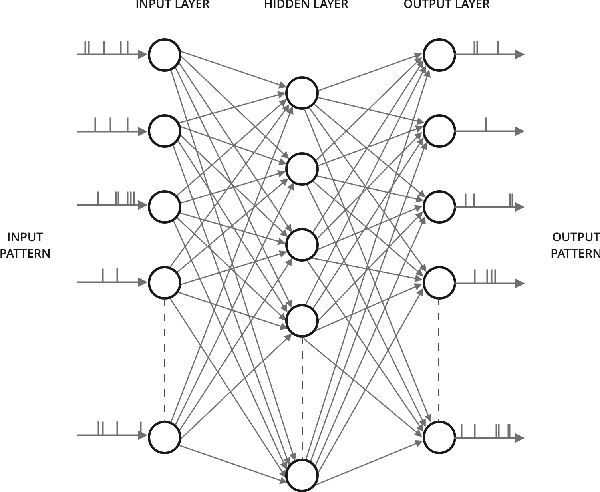
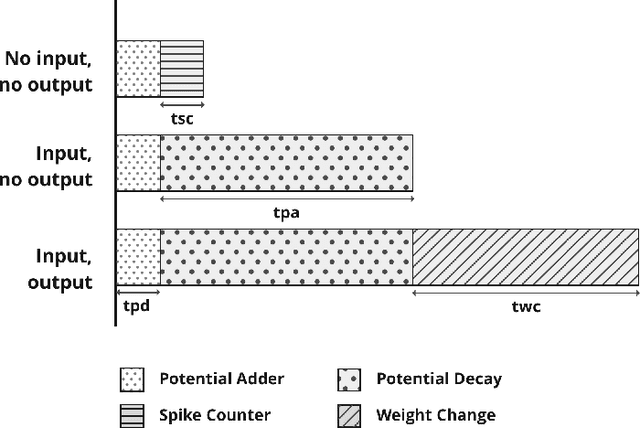
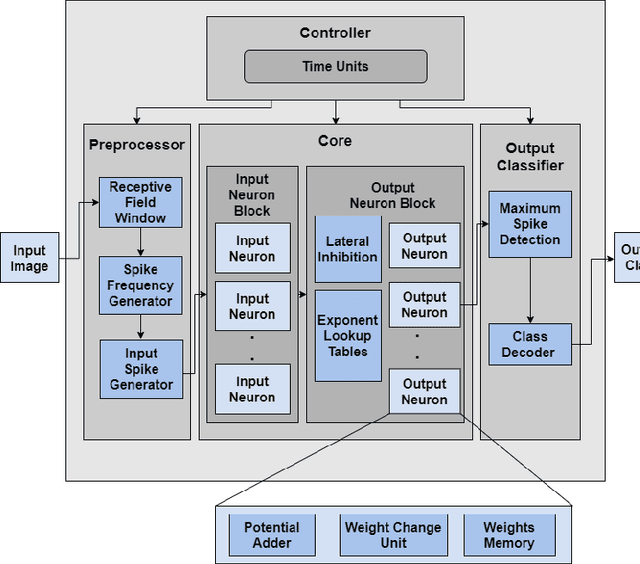

Spiking Neural Networks (SNN) are third-generation Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) which are close to the biological neural system. In recent years SNN has become popular in the area of robotics and embedded applications, therefore, it has become imperative to explore its real-time and energy-efficient implementations. SNNs are more powerful than their predecessors because they encode temporal information and use biologically plausible plasticity rules. In this paper, a simpler and computationally efficient SNN model using FPGA architecture is described. The proposed model is validated on a Xilinx Virtex 6 FPGA and analyzes a fully connected network which consists of 800 neurons and 12,544 synapses in real-time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge