Extract fundamental frequency based on CNN combined with PYIN
Paper and Code
Aug 17, 2022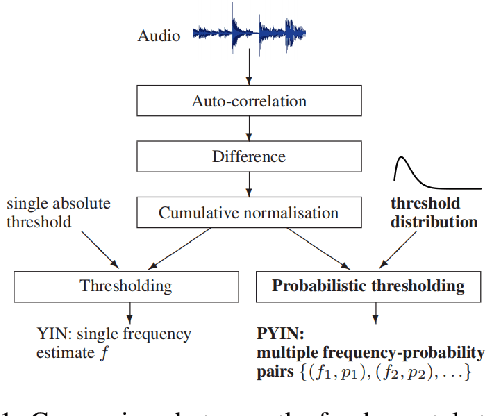
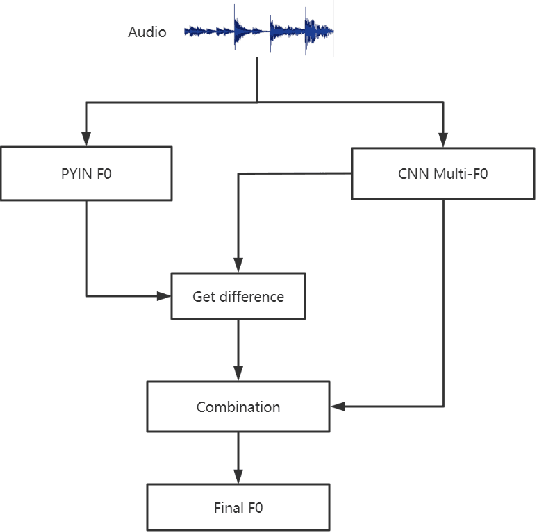
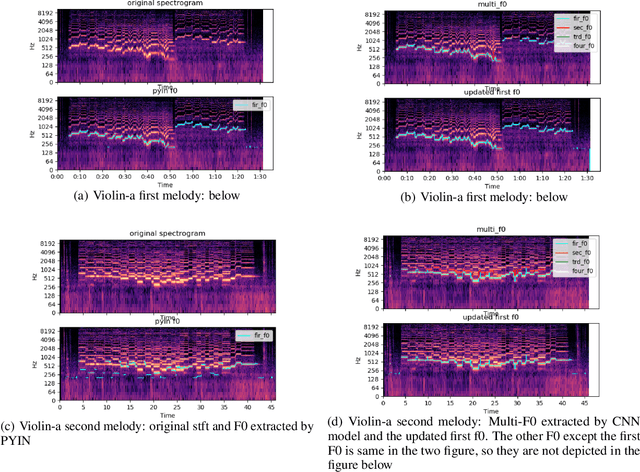
This paper refers to the extraction of multiple fundamental frequencies (multiple F0) based on PYIN, an algorithm for extracting the fundamental frequency (F0) of monophonic music, and a trained convolutional neural networks (CNN) model, where a pitch salience function of the input signal is produced to estimate the multiple F0. The implementation of these two algorithms and their corresponding advantages and disadvantages are discussed in this article. Analysing the different performance of these two methods, PYIN is applied to supplement the F0 extracted from the trained CNN model to combine the advantages of these two algorithms. For evaluation, four pieces played by two violins are used, and the performance of the models are evaluated accoring to the flatness of the F0 curve extracted. The result shows the combined model outperforms the original algorithms when extracting F0 from monophonic music and polyphonic music.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge