Exploring the Connection between Robust and Generative Models
Paper and Code
Apr 08, 2023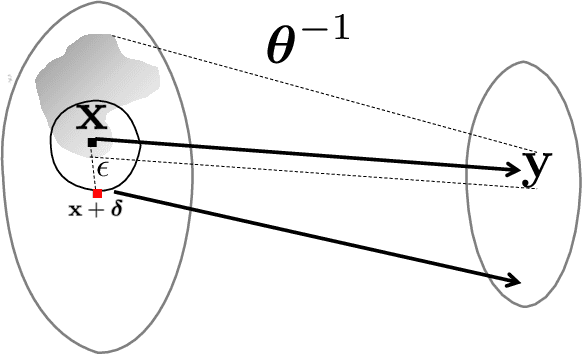
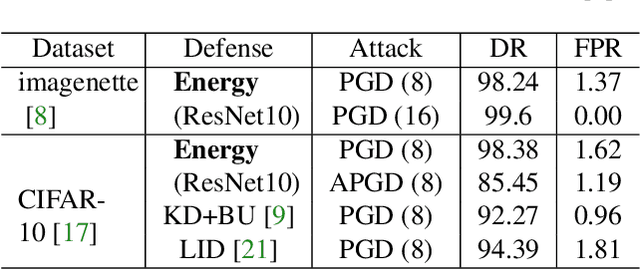
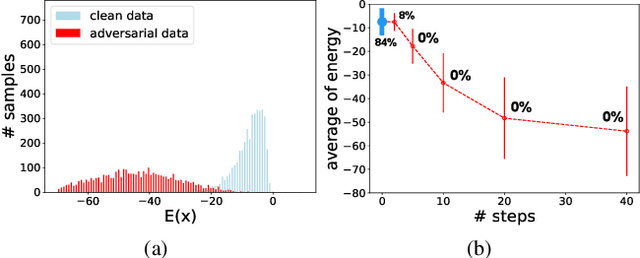
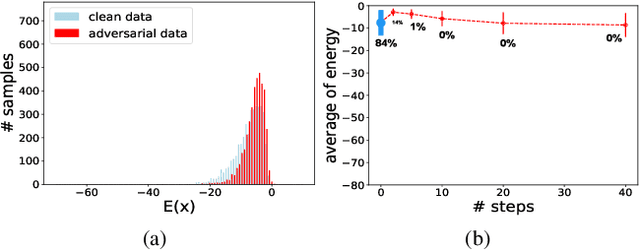
We offer a study that connects robust discriminative classifiers trained with adversarial training (AT) with generative modeling in the form of Energy-based Models (EBM). We do so by decomposing the loss of a discriminative classifier and showing that the discriminative model is also aware of the input data density. Though a common assumption is that adversarial points leave the manifold of the input data, our study finds out that, surprisingly, untargeted adversarial points in the input space are very likely under the generative model hidden inside the discriminative classifier -- have low energy in the EBM. We present two evidence: untargeted attacks are even more likely than the natural data and their likelihood increases as the attack strength increases. This allows us to easily detect them and craft a novel attack called High-Energy PGD that fools the classifier yet has energy similar to the data set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge