Encoding information in the mutual coherence of spatially separated light beams
Paper and Code
Aug 02, 2022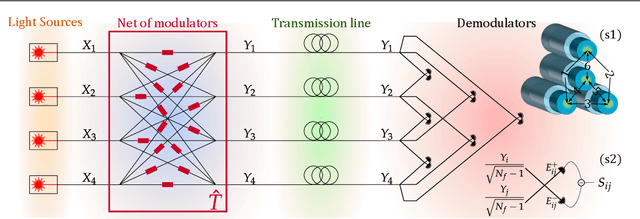
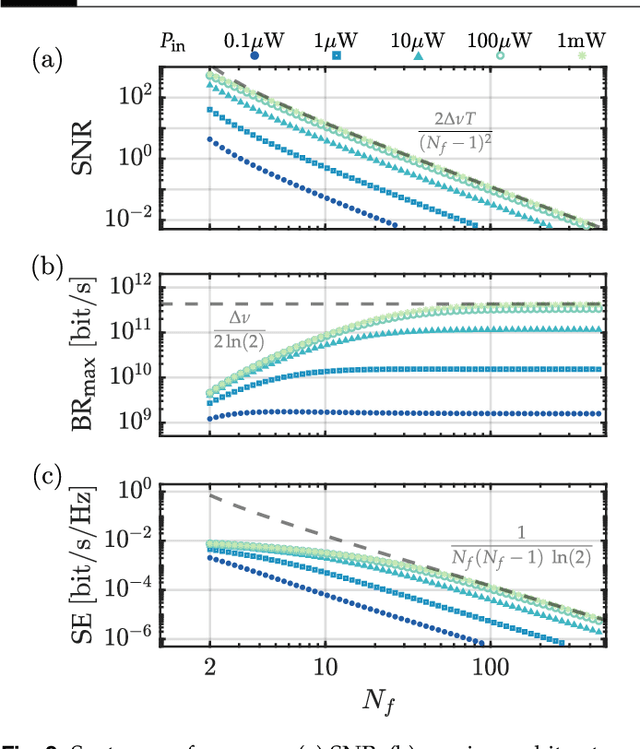
Coherence has been used as a resource for optical communications since its earliest days. It is widely used for multiplexing of data, but not for encoding of data. Here we introduce a coding scheme, which we call \textit{mutual coherence coding}, to encode information in the mutual coherence of spatially separated light beams. We describe its implementation and analyze its performance by deriving the relevant figures of merit (signal-to-noise ratio, maximum bit-rate, and spectral efficiency) with respect to the number of transmitted beams. Mutual coherence coding yields a quadratic scaling of the number of transmitted signals with the number of employed light beams, which might have benefits for cryptography and data security.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge