Emergence through Selection: The Evolution of a Scientific Challenge
Paper and Code
Feb 01, 2011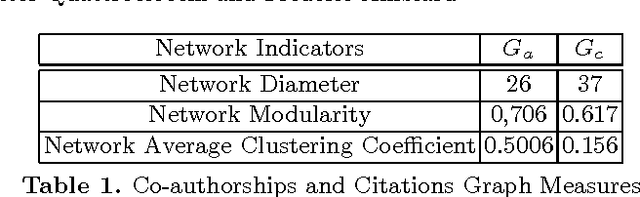
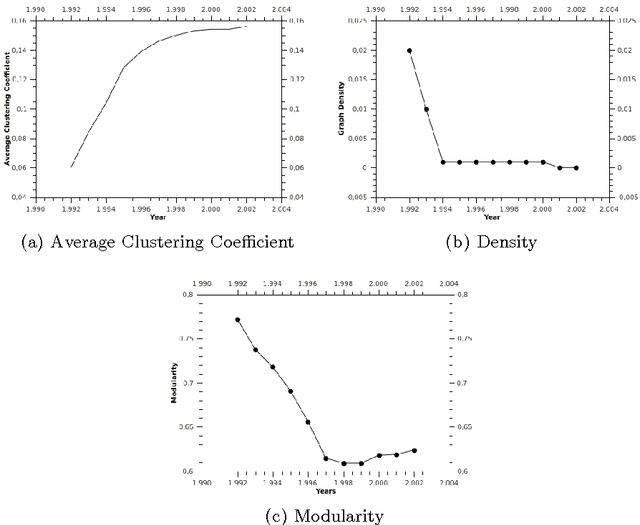
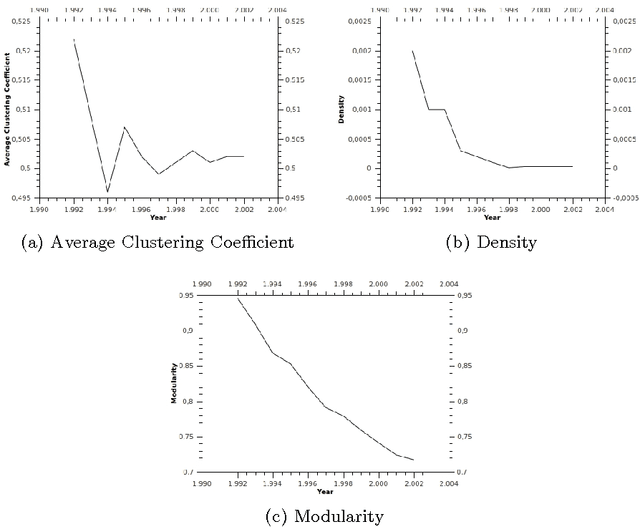
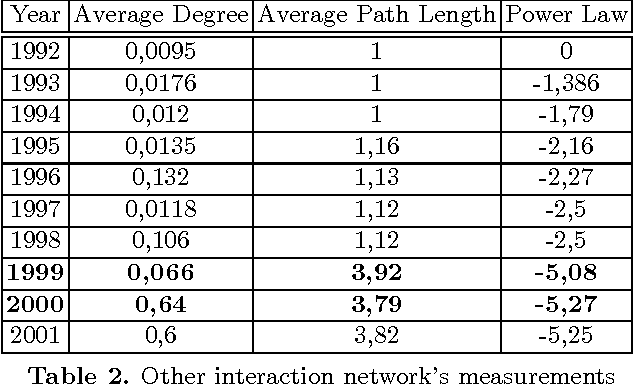
One of the most interesting scientific challenges nowadays deals with the analysis and the understanding of complex networks' dynamics and how their processes lead to emergence according to the interactions among their components. In this paper we approach the definition of new methodologies for the visualization and the exploration of the dynamics at play in real dynamic social networks. We present a recently introduced formalism called TVG (for time-varying graphs), which was initially developed to model and analyze highly-dynamic and infrastructure-less communication networks such as mobile ad-hoc networks, wireless sensor networks, or vehicular networks. We discuss its applicability to complex networks in general, and social networks in particular, by showing how it enables the specification and analysis of complex dynamic phenomena in terms of temporal interactions, and allows to easily switch the perspective between local and global dynamics. As an example, we chose the case of scientific communities by analyzing portion of the ArXiv repository (ten years of publications in physics) focusing on the social determinants (e.g. goals and potential interactions among individuals) behind the emergence and the resilience of scientific communities. We consider that scientific communities are at the same time communities of practice (through co-authorship) and that they exist also as representations in the scientists' mind, since references to other scientists' works is not merely an objective link to a relevant work, but it reveals social objects that one manipulates, select and refers to. In the paper we show the emergence/selection of a community as a goal-driven preferential attachment toward a set of authors among which there are some key scientists (Nobel prizes).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge