Efficient Tree Solver for Hines Matrices on the GPU
Paper and Code
Nov 06, 2018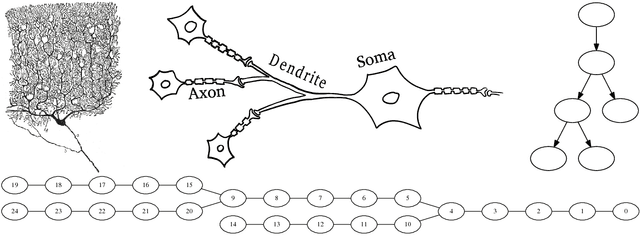
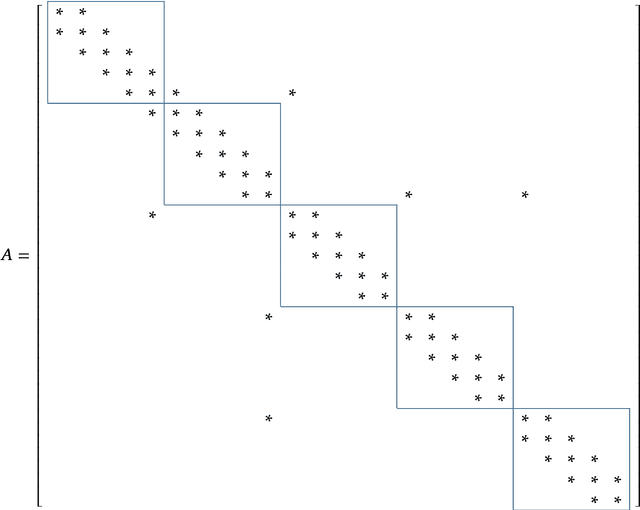
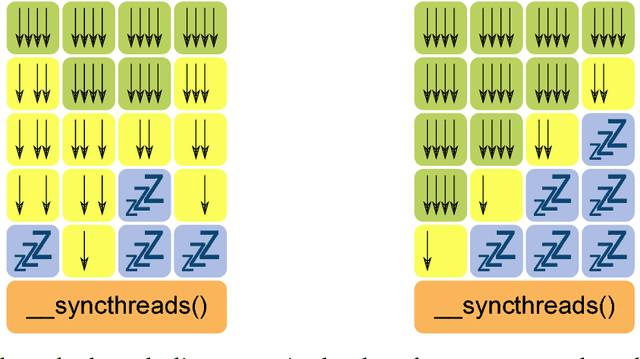
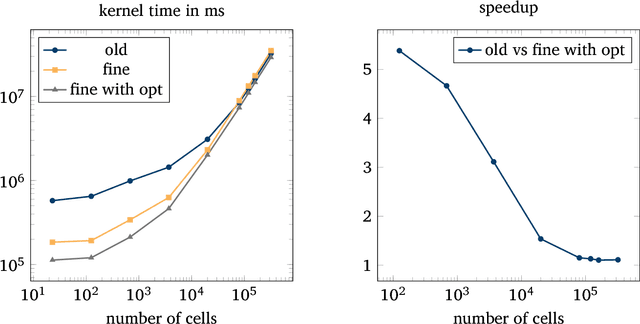
The human brain consists of a large number of interconnected neurons communicating via exchange of electrical spikes. Simulations play an important role in better understanding electrical activity in the brain and offers a way to to compare measured data to simulated data such that experimental data can be interpreted better. A key component in such simulations is an efficient solver for the Hines matrices used in computing inter-neuron signal propagation. In order to achieve high performance simulations, it is crucial to have an efficient solver algorithm. In this report we explain a new parallel GPU solver for these matrices which offers fine grained parallelization and allows for work balancing during the simulation setup.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge