EDCA -- An Evolutionary Data-Centric AutoML Framework for Efficient Pipelines
Paper and Code
Mar 06, 2025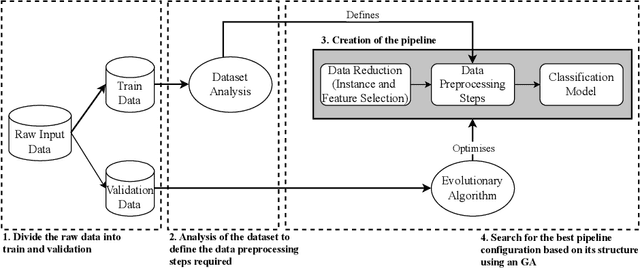
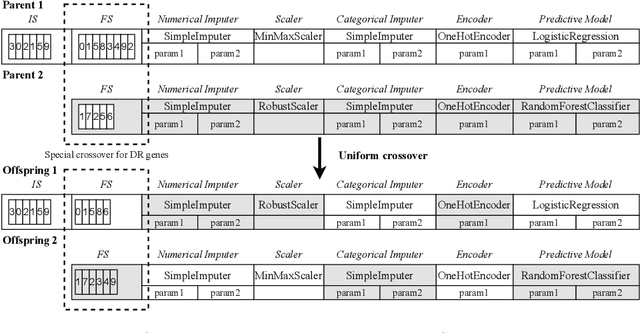
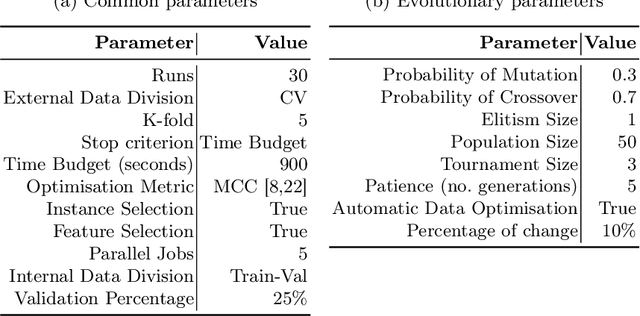
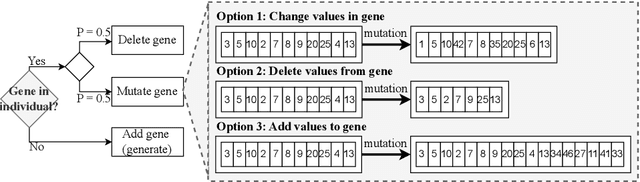
Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) gained popularity due to the increased demand for Machine Learning (ML) specialists, allowing them to apply ML techniques effortlessly and quickly. AutoML implementations use optimisation methods to identify the most effective ML solution for a given dataset, aiming to improve one or more predefined metrics. However, most implementations focus on model selection and hyperparameter tuning. Despite being an important factor in obtaining high-performance ML systems, data quality is usually an overlooked part of AutoML and continues to be a manual and time-consuming task. This work presents EDCA, an Evolutionary Data Centric AutoML framework. In addition to the traditional tasks such as selecting the best models and hyperparameters, EDCA enhances the given data by optimising data processing tasks such as data reduction and cleaning according to the problems' needs. All these steps create an ML pipeline that is optimised by an evolutionary algorithm. To assess its effectiveness, EDCA was compared to FLAML and TPOT, two frameworks at the top of the AutoML benchmarks. The frameworks were evaluated in the same conditions using datasets from AMLB classification benchmarks. EDCA achieved statistically similar results in performance to FLAML and TPOT but used significantly less data to train the final solutions. Moreover, EDCA experimental results reveal that a good performance can be achieved using less data and efficient ML algorithm aspects that align with Green AutoML guidelines
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge