Don't Discard Fixed-Window Audio Segmentation in Speech-to-Text Translation
Paper and Code
Oct 24, 2022
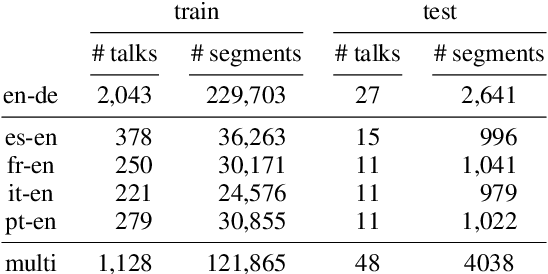
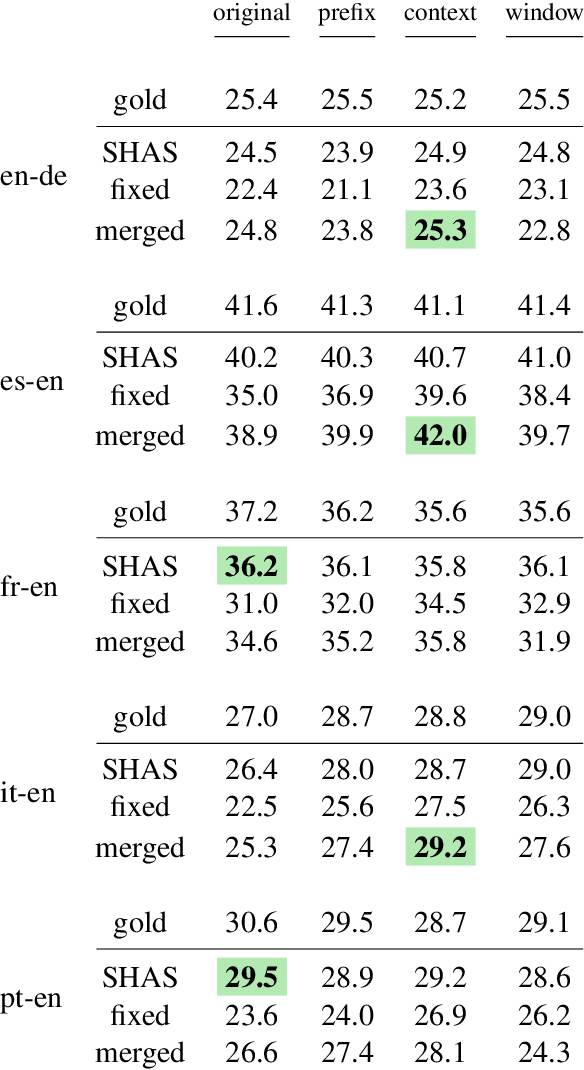
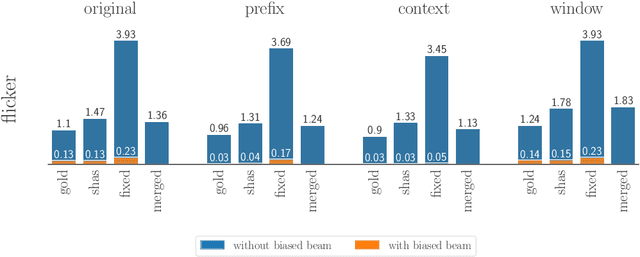
For real-life applications, it is crucial that end-to-end spoken language translation models perform well on continuous audio, without relying on human-supplied segmentation. For online spoken language translation, where models need to start translating before the full utterance is spoken, most previous work has ignored the segmentation problem. In this paper, we compare various methods for improving models' robustness towards segmentation errors and different segmentation strategies in both offline and online settings and report results on translation quality, flicker and delay. Our findings on five different language pairs show that a simple fixed-window audio segmentation can perform surprisingly well given the right conditions.
* accepted to WMT22
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge