Detecting mechanical loosening of total hip replacement implant from plain radiograph using deep convolutional neural network
Paper and Code
Dec 02, 2019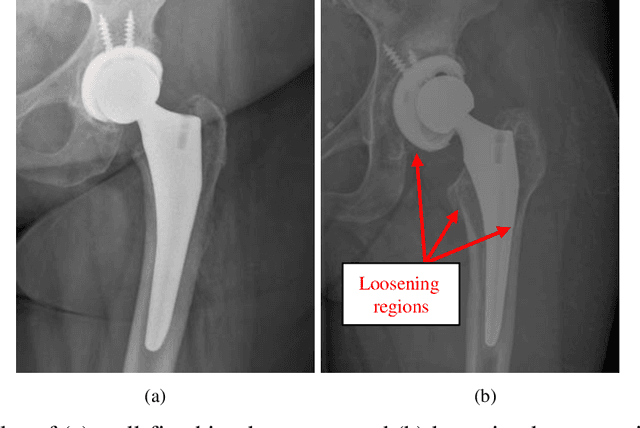
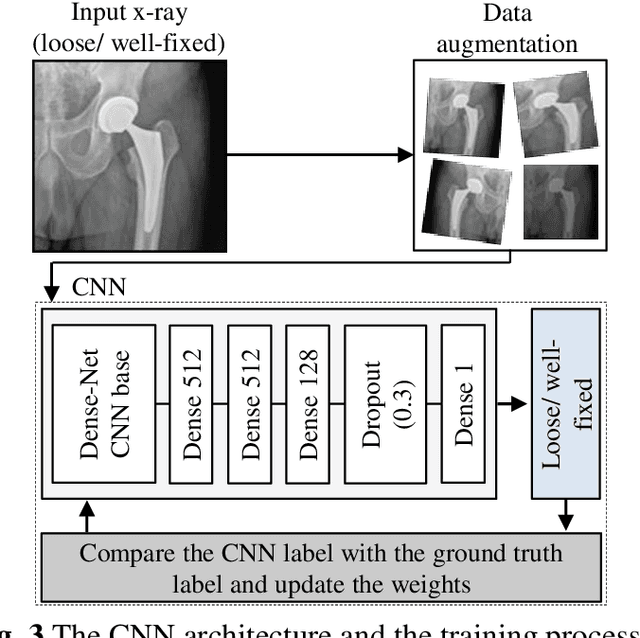
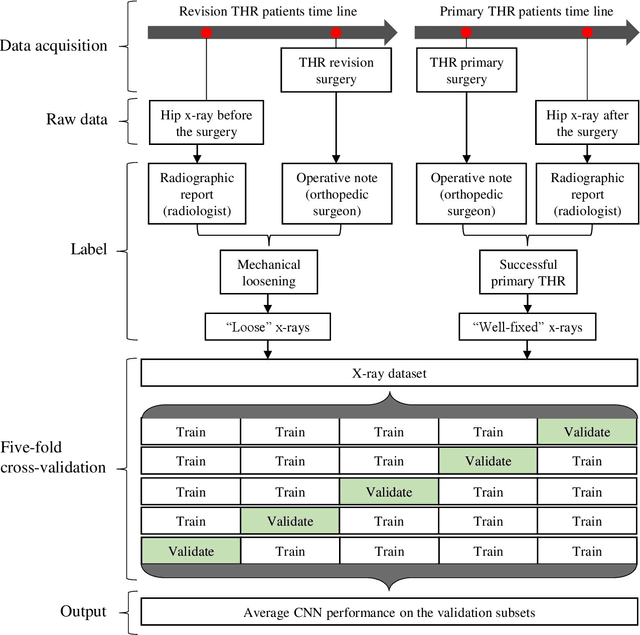
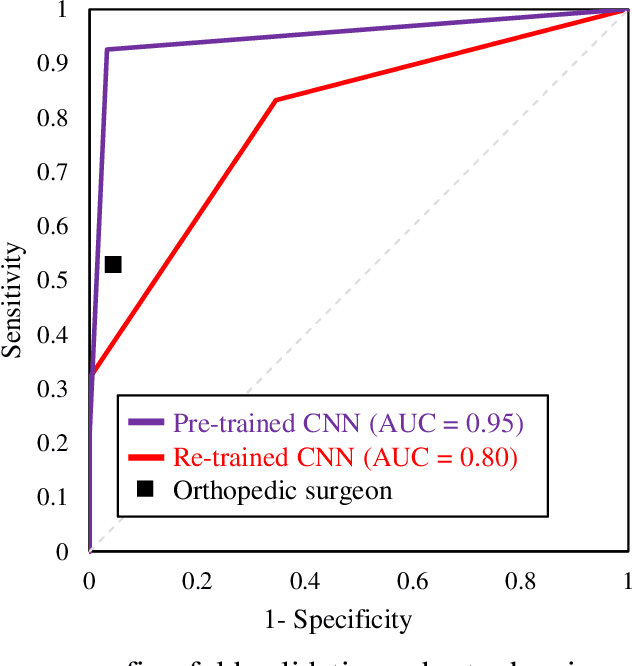
Plain radiography is widely used to detect mechanical loosening of total hip replacement (THR) implants. Currently, radiographs are assessed manually by medical professionals, which may be prone to poor inter and intra observer reliability and low accuracy. Furthermore, manual detection of mechanical loosening of THR implants requires experienced clinicians who might not always be readily available, potentially resulting in delayed diagnosis. In this study, we present a novel, fully automatic and interpretable approach to detect mechanical loosening of THR implants from plain radiographs using deep convolutional neural network (CNN). We trained a CNN on 40 patients anteroposterior hip x rays using five fold cross validation and compared its performance with a high volume board certified orthopaedic surgeon (AFC). To increase the confidence in the machine outcome, we also implemented saliency maps to visualize where the CNN looked at to make a diagnosis. CNN outperformed the orthopaedic surgeon in diagnosing mechanical loosening of THR implants achieving significantly higher sensitively (0.94) than the orthopaedic surgeon (0.53) with the same specificity (0.96). The saliency maps showed that the CNN looked at clinically relevant features to make a diagnosis. Such CNNs can be used for automatic radiologic assessment of mechanical loosening of THR implants to supplement the practitioners decision making process, increasing their diagnostic accuracy, and freeing them to engage in more patient centric care.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge