Cross-Discourse and Multilingual Exploration of Textual Corpora with the DualNeighbors Algorithm
Paper and Code
Jun 28, 2018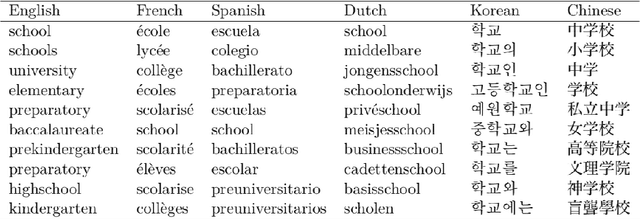

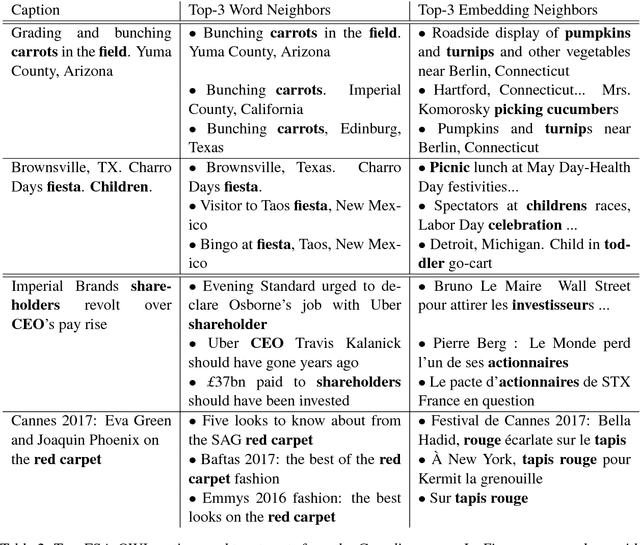
Word choice is dependent on the cultural context of writers and their subjects. Different words are used to describe similar actions, objects, and features based on factors such as class, race, gender, geography and political affinity. Exploratory techniques based on locating and counting words may, therefore, lead to conclusions that reinforce culturally inflected boundaries. We offer a new method, the DualNeighbors algorithm, for linking thematically similar documents both within and across discursive and linguistic barriers to reveal cross-cultural connections. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations of this technique are shown as applied to two cultural datasets of interest to researchers across the humanities and social sciences. An open-source implementation of the DualNeighbors algorithm is provided to assist in its application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge