Comparisons of wavelet functions in QRS signal to noise ratio enhancement and detection accuracy
Paper and Code
Apr 16, 2015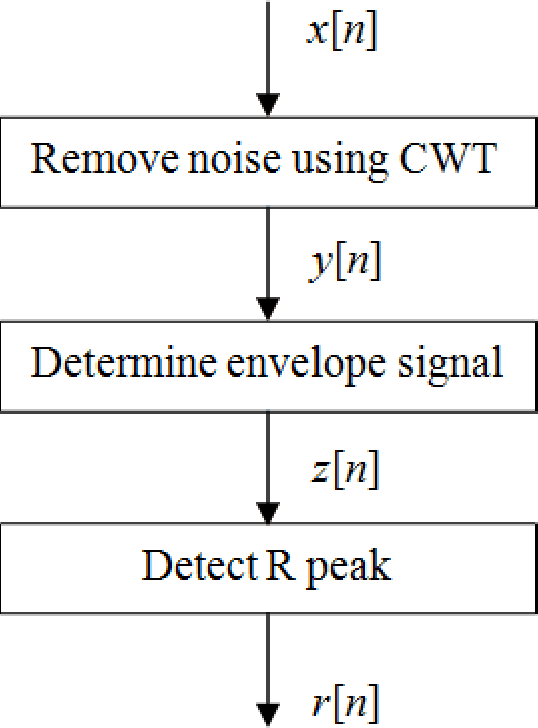
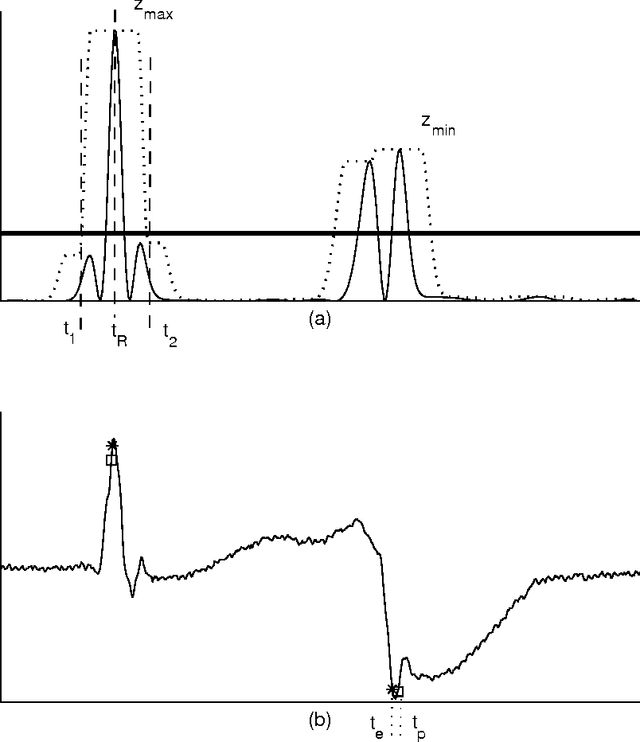
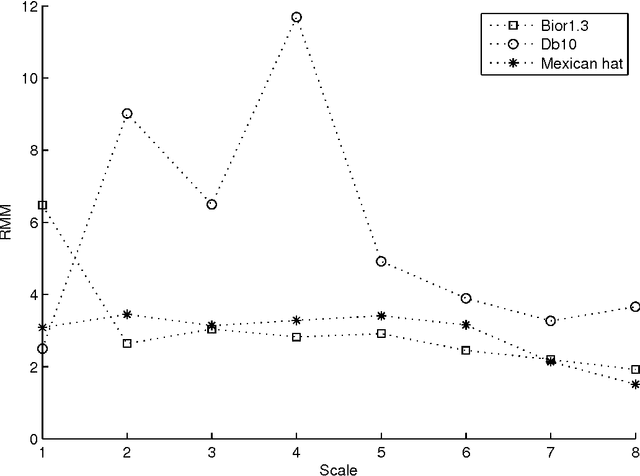
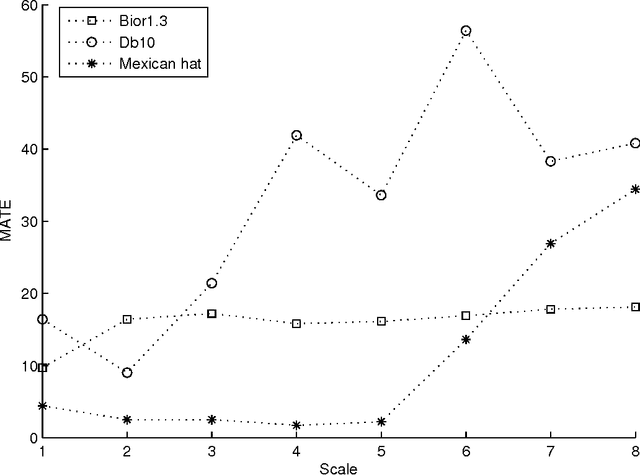
We compare the capability of wavelet functions used for noise removal in preprocessing step of a QRS detection algorithm in the electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The QRS signal to noise ratio enhancement and the detection accuracy of each wavelet function are evaluated using three measures: (1) the ratio of the maximum beat amplitude to the minimum beat amplitude (RMM), (2) the mean of absolute of time error (MATE), and (3) the figure of merit (FOM). Three wavelet functions from previous well-known publications are explored, i.e., Bior1.3, Db10, and Mexican hat wavelet functions. Results evaluated with the ECG signal from MIT-BIH arrhythmia database show that the Mexican hat wavelet function is better than the others. While the scale 8 of Mexican hat wavelet function can provide the best enhancement in QRS signal to noise ratio, the scale 4 of Mexican hat wavelet function can provide the best detection accuracy. These results may be combined and may enable the use of a single fixed threshold for all ECG records leading to the reduction in computational complexity of the QRS detection algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge