Cluster Representatives Selection in Non-Metric Spaces for Nearest Prototype Classification
Paper and Code
Jul 03, 2021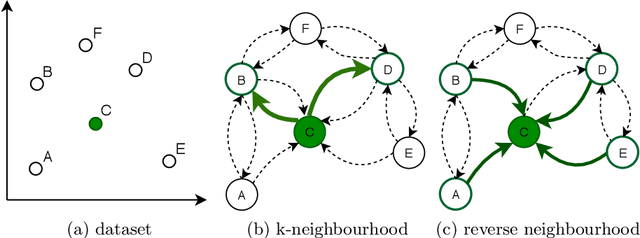
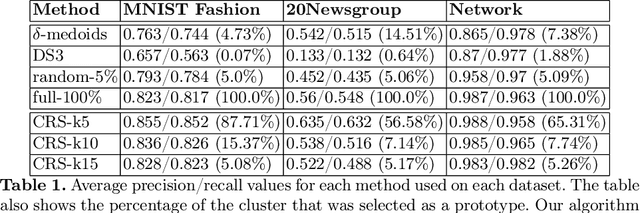
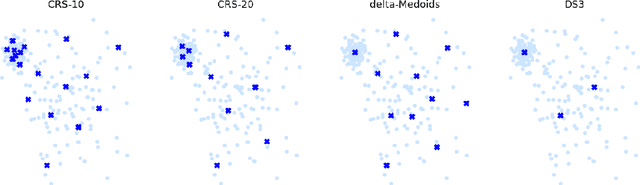
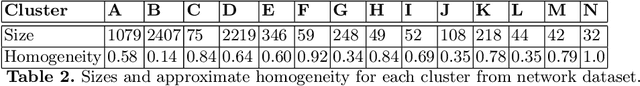
The nearest prototype classification is a less computationally intensive replacement for the $k$-NN method, especially when large datasets are considered. In metric spaces, centroids are often used as prototypes to represent whole clusters. The selection of cluster prototypes in non-metric spaces is more challenging as the idea of computing centroids is not directly applicable. In this paper, we present CRS, a novel method for selecting a small yet representative subset of objects as a cluster prototype. Memory and computationally efficient selection of representatives is enabled by leveraging the similarity graph representation of each cluster created by the NN-Descent algorithm. CRS can be used in an arbitrary metric or non-metric space because of the graph-based approach, which requires only a pairwise similarity measure. As we demonstrate in the experimental evaluation, our method outperforms the state of the art techniques on multiple datasets from different domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge