Benchmarking Monocular 3D Dog Pose Estimation Using In-The-Wild Motion Capture Data
Paper and Code
Jun 20, 2024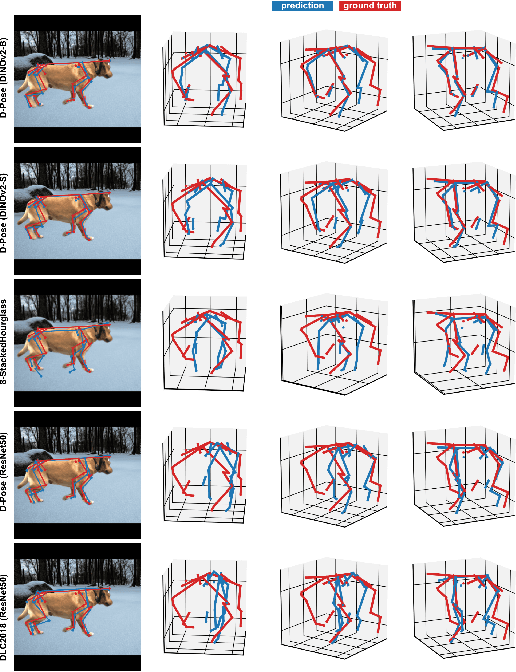
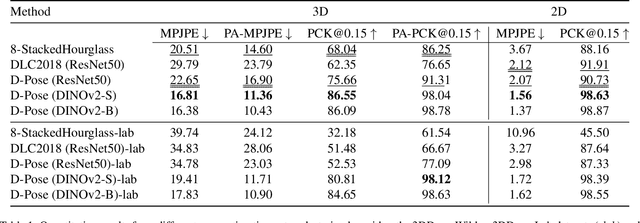

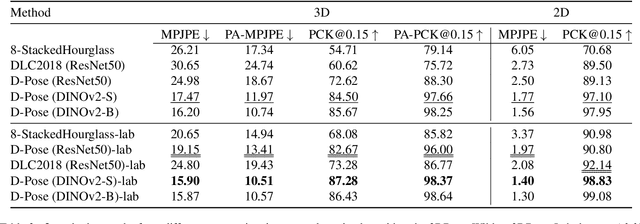
We introduce a new benchmark analysis focusing on 3D canine pose estimation from monocular in-the-wild images. A multi-modal dataset 3DDogs-Lab was captured indoors, featuring various dog breeds trotting on a walkway. It includes data from optical marker-based mocap systems, RGBD cameras, IMUs, and a pressure mat. While providing high-quality motion data, the presence of optical markers and limited background diversity make the captured video less representative of real-world conditions. To address this, we created 3DDogs-Wild, a naturalised version of the dataset where the optical markers are in-painted and the subjects are placed in diverse environments, enhancing its utility for training RGB image-based pose detectors. We show that using the 3DDogs-Wild to train the models leads to improved performance when evaluating on in-the-wild data. Additionally, we provide a thorough analysis using various pose estimation models, revealing their respective strengths and weaknesses. We believe that our findings, coupled with the datasets provided, offer valuable insights for advancing 3D animal pose estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge