Benchmarking learned non-Cartesian k-space trajectories and reconstruction networks
Paper and Code
Jan 27, 2022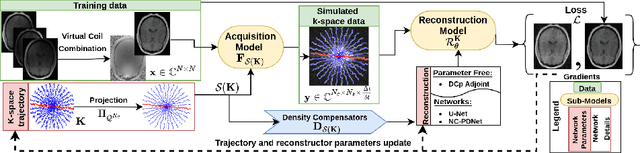
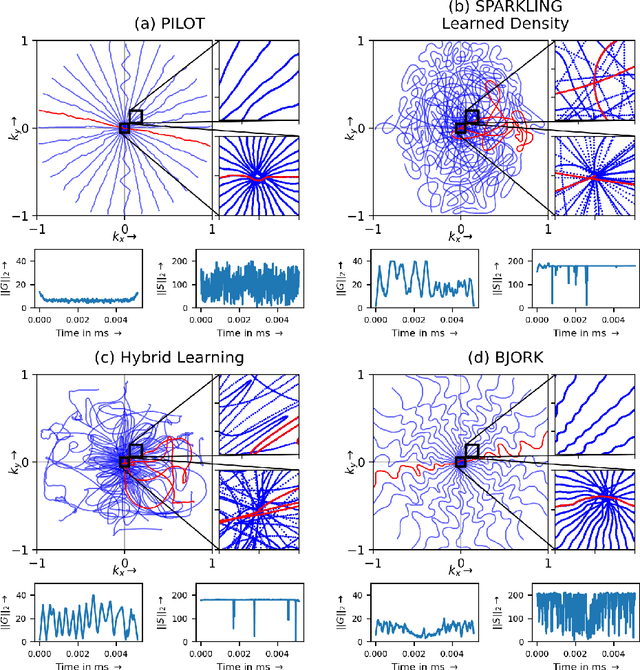

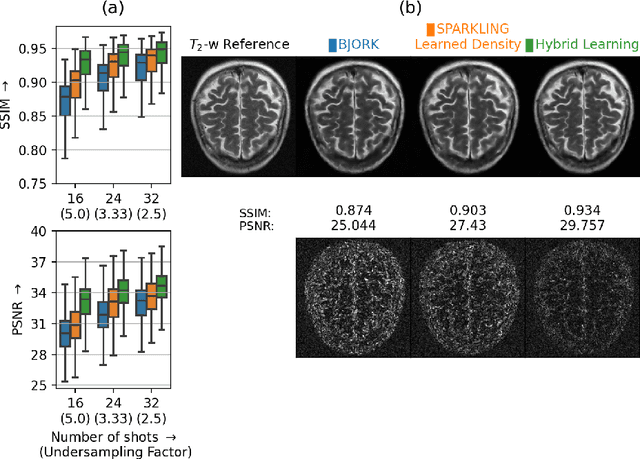
We benchmark the current existing methods to jointly learn non-Cartesian k-space trajectory and reconstruction: PILOT, BJORK, and compare them with those obtained from the recently developed generalized hybrid learning (HybLearn) framework. We present the advantages of using projected gradient descent to enforce MR scanner hardware constraints as compared to using added penalties in the cost function. Further, we use the novel HybLearn scheme to jointly learn and compare our results through a retrospective study on fastMRI validation dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge