Bad and good errors: value-weighted skill scores in deep ensemble learning
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2021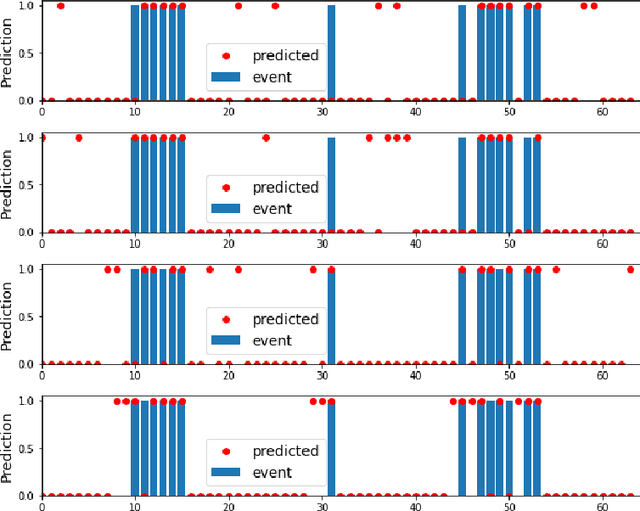
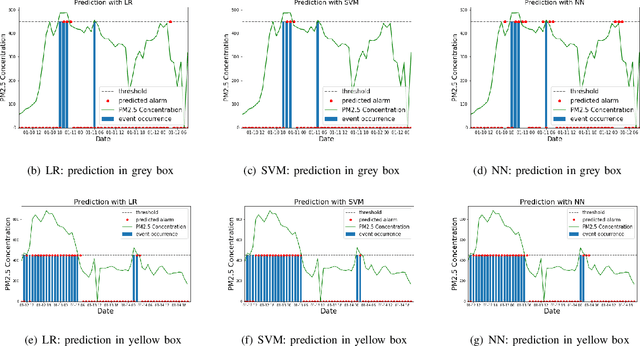
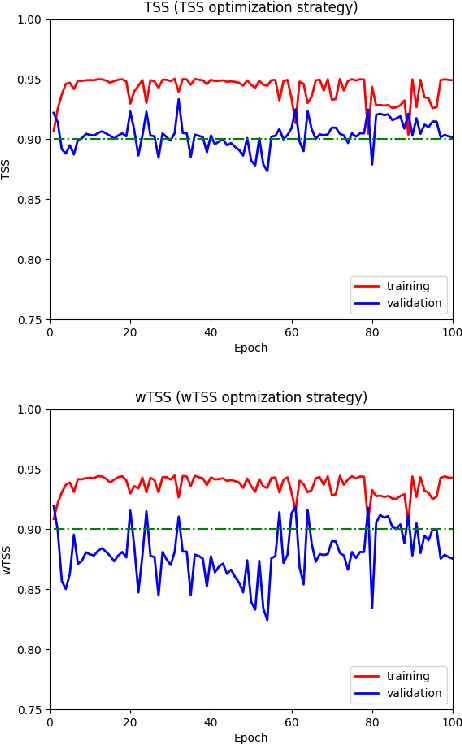
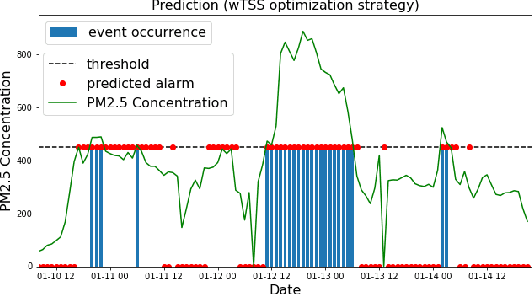
In this paper we propose a novel approach to realize forecast verification. Specifically, we introduce a strategy for assessing the severity of forecast errors based on the evidence that, on the one hand, a false alarm just anticipating an occurring event is better than one in the middle of consecutive non-occurring events, and that, on the other hand, a miss of an isolated event has a worse impact than a miss of a single event, which is part of several consecutive occurrences. Relying on this idea, we introduce a novel definition of confusion matrix and skill scores giving greater importance to the value of the prediction rather than to its quality. Then, we introduce a deep ensemble learning procedure for binary classification, in which the probabilistic outcomes of a neural network are clustered via optimization of these value-weighted skill scores. We finally show the performances of this approach in the case of three applications concerned with pollution, space weather and stock prize forecasting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge