Automatically Inferring Gender Associations from Language
Paper and Code
Aug 30, 2019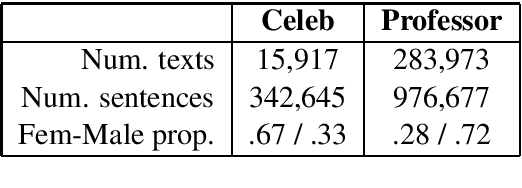
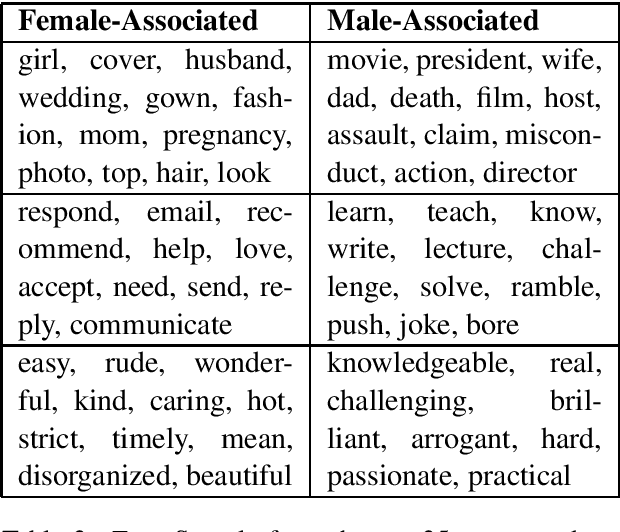
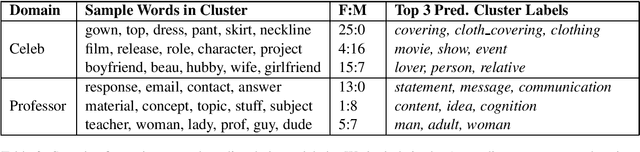
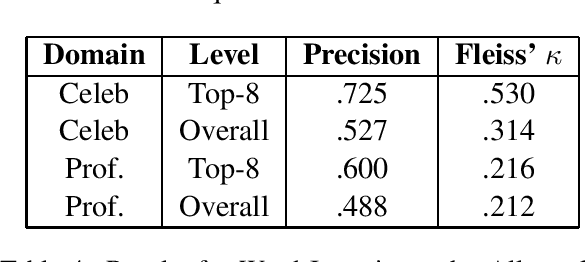
In this paper, we pose the question: do people talk about women and men in different ways? We introduce two datasets and a novel integration of approaches for automatically inferring gender associations from language, discovering coherent word clusters, and labeling the clusters for the semantic concepts they represent. The datasets allow us to compare how people write about women and men in two different settings - one set draws from celebrity news and the other from student reviews of computer science professors. We demonstrate that there are large-scale differences in the ways that people talk about women and men and that these differences vary across domains. Human evaluations show that our methods significantly outperform strong baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge