Autoencoder based approach for the mitigation of spurious correlations
Paper and Code
Jun 27, 2024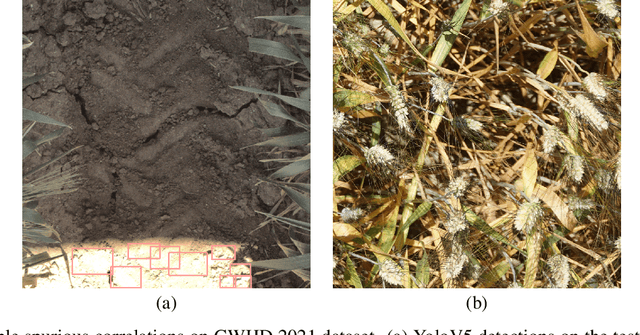
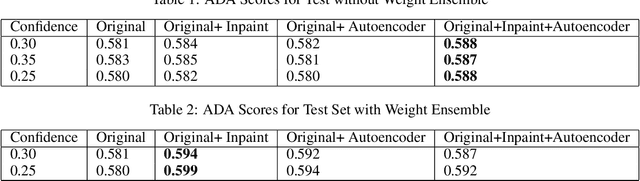
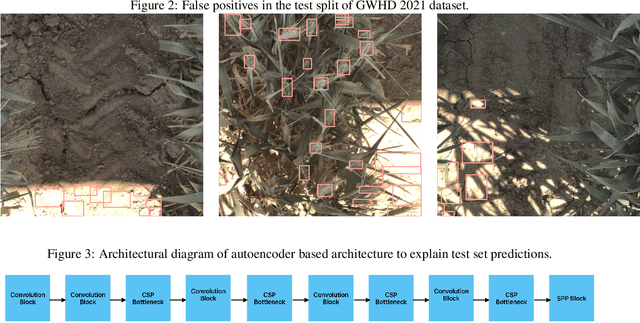

Deep neural networks (DNNs) have exhibited remarkable performance across various tasks, yet their susceptibility to spurious correlations poses a significant challenge for out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization. Spurious correlations refer to erroneous associations in data that do not reflect true underlying relationships but are instead artifacts of dataset characteristics or biases. These correlations can lead DNNs to learn patterns that are not robust across diverse datasets or real-world scenarios, hampering their ability to generalize beyond training data. In this paper, we propose an autoencoder-based approach to analyze the nature of spurious correlations that exist in the Global Wheat Head Detection (GWHD) 2021 dataset. We then use inpainting followed by Weighted Boxes Fusion (WBF) to achieve a 2% increase in the Average Domain Accuracy (ADA) over the YOLOv5 baseline and consistently show that our approach has the ability to suppress some of the spurious correlations in the GWHD 2021 dataset. The key advantage of our approach is that it is more suitable in scenarios where there is limited scope to adapt or fine-tune the trained model in unseen test environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge