Application and Comparison of Deep Learning Methods in the Prediction of RNA Sequence Degradation and Stability
Paper and Code
Nov 09, 2020
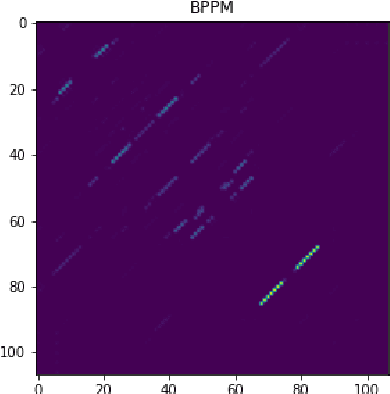

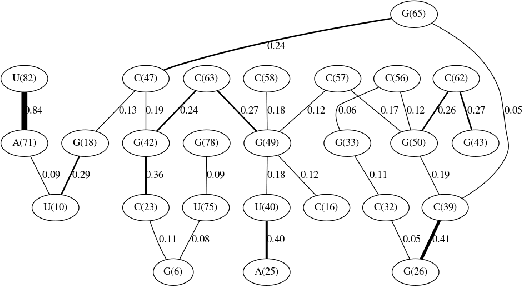
mRNA vaccines are receiving increased interest as potential alternatives to conventional methods for the prevention of several diseases, including Covid-19. This paper proposes and evaluates three deep learning models (Long Short Term Memory networks, Gated Recurrent Unit networks, and Graph Convolutional Networks) as a method to predict the stability/reactivity and risk of degradation of sequences of RNA. Reasonably accurate results were able to be generated, with the Graph Convolutional Network being the best predictor of reactivity (RMSE = 0.249) while the Gated Recurrent Unit Network was the best at predicting risks of degradation under various circumstances (RMSE = 0.266). Results suggest feasibility of applying such methods in mRNA vaccine research in the near future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge