Anomaly Detection for Solder Joints Using $β$-VAE
Paper and Code
Apr 24, 2021
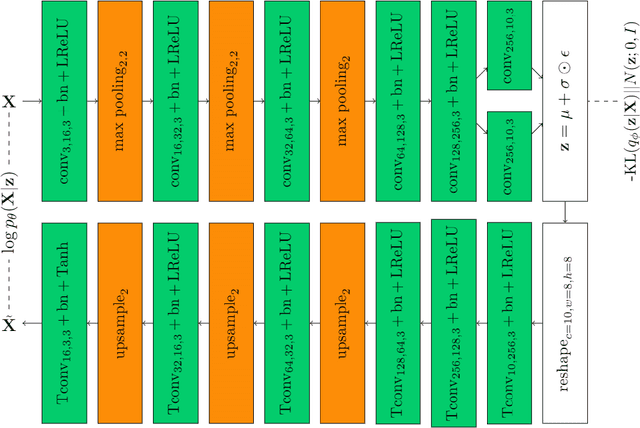
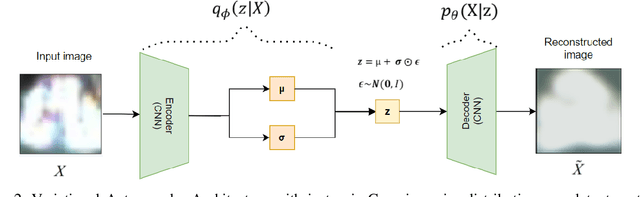


In the assembly process of printed circuit boards (PCB), most of the errors are caused by solder joints in Surface Mount Devices (SMD). In the literature, traditional feature extraction based methods require designing hand-crafted features and rely on the tiered RGB illumination to detect solder joint errors, whereas the supervised Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based approaches require a lot of labelled abnormal samples (defective solder joints) to achieve high accuracy. To solve the optical inspection problem in unrestricted environments with no special lighting and without the existence of error-free reference boards, we propose a new beta-Variational Autoencoders (beta-VAE) architecture for anomaly detection that can work on both IC and non-IC components. We show that the proposed model learns disentangled representation of data, leading to more independent features and improved latent space representations. We compare the activation and gradient-based representations that are used to characterize anomalies; and observe the effect of different beta parameters on accuracy and on untwining the feature representations in beta-VAE. Finally, we show that anomalies on solder joints can be detected with high accuracy via a model trained on directly normal samples without designated hardware or feature engineering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge