Analysis of Total Variation Minimization for Clustered Federated Learning
Paper and Code
Mar 10, 2024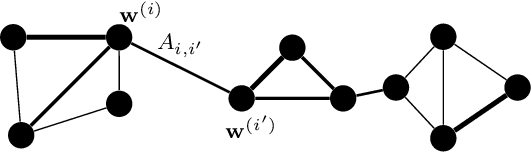
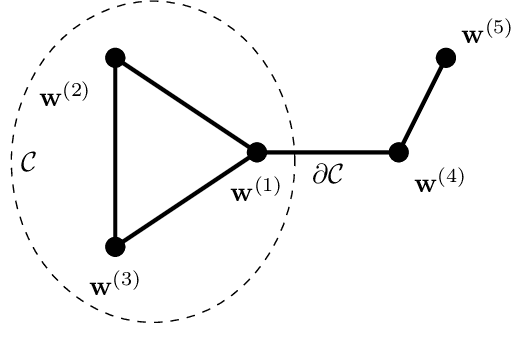
A key challenge in federated learning applications is the statistical heterogeneity of local datasets. Clustered federated learning addresses this challenge by identifying clusters of local datasets that are approximately homogeneous. One recent approach to clustered federated learning is generalized total variation minimization (GTVMin). This approach requires a similarity graph which can be obtained by domain expertise or in a data-driven fashion via graph learning techniques. Under a widely applicable clustering assumption, we derive an upper bound the deviation between GTVMin solutions and their cluster-wise averages. This bound provides valuable insights into the effectiveness and robustness of GTVMin in addressing statistical heterogeneity within federated learning environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge