An exploration of asocial and social learning in the evolution of variable-length structures
Paper and Code
Apr 16, 2021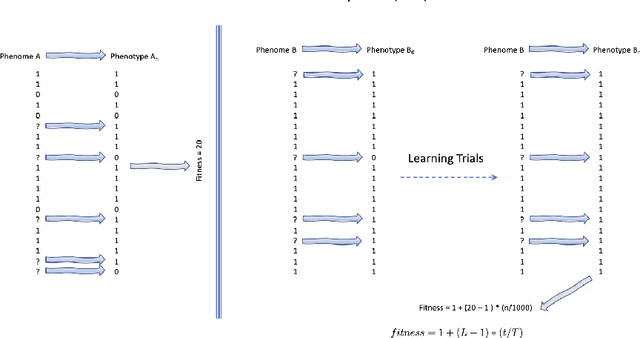
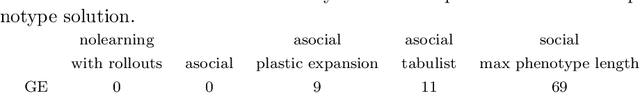
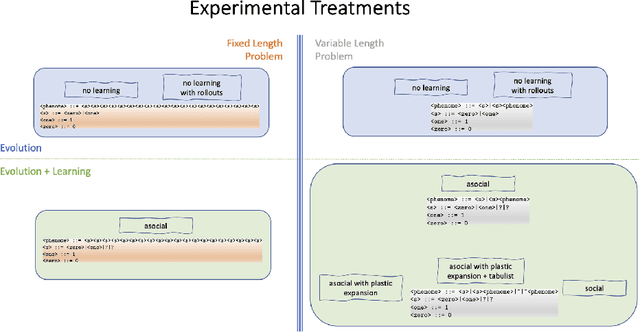
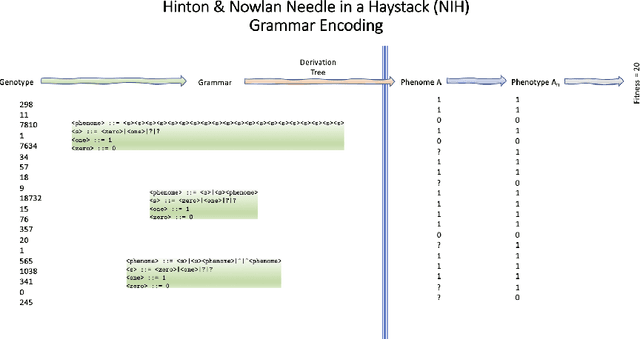
We wish to explore the contribution that asocial and social learning might play as a mechanism for self-adaptation in the search for variable-length structures by an evolutionary algorithm. An extremely challenging, yet simple to understand problem landscape is adopted where the probability of randomly finding a solution is approximately one in a trillion. A number of learning mechanisms operating on variable-length structures are implemented and their performance analysed. The social learning setup, which combines forms of both social and asocial learning in combination with evolution is found to be most performant, while the setups exclusively adopting evolution are incapable of finding solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge